When researching clinical trial-related documents, you may come across the term CTD (Common Technical Document). Among clinical trial-related documents, the CTD is considered a document with high translation demand, following the Clinical Trial Protocol, Investigator's Brochure, and Clinical Study Report. In this blog, we will introduce what the CTD is and key points about CTD translation.
- Table of Contents
-
- 1. What is CTD? What is the background of CTD?
- 1-1. What is CTD?
- 1-2. Background of CTD Creation
- 1-3. Movement towards digitization in CTD (eCTD)
- 2. Structure of the CTD
- 3. Cases Requiring CTD Translation and Important Points to Note in Translation
- 3-1. Cases Where CTD Translation (Japanese to English) Is Required
- 3-2. Notes on CTD Translation
- 4. Key Points for Efficiently Advancing CTD Translation – Selecting the Right Medical Translation Company is Crucial
- 5. Please also entrust CTD translation to Human Science
1. What is CTD? What is the background of CTD?

1-1. What is CTD?
CTD stands for Common Technical Document. It is a set of documents used by pharmaceutical companies to apply for drug approval to regulatory authorities in various countries and regions. It has been internationally standardized across Japan, the US, and the EU, compiling extensive documents including information on pharmaceuticals, clinical trials, and various application forms. The introduction of the CTD was significantly influenced by the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) in Japan, the US, and the EU. Since 2001, approval applications using the CTD have been submitted.
1-2. Background of CTD Creation
CTD is easier to understand when you know its purpose and background.
Traditionally, it was necessary to create and edit different approval application documents for each region: Japan, the US, and the EU. CTD aims to avoid differing application contents and formats across these three regions.
Using internationally standardized documents and formats for pharmaceutical applications leads to more efficient drug development and faster application and approval processes in each country and region, directly benefiting patients' recovery and health, as well as regulatory agencies and pharmaceutical companies.
In that sense, the development and implementation of CTD can be said to have been eagerly awaited by patients, regulatory agencies, and pharmaceutical companies alike.
1-3. Movement towards digitization in CTD (eCTD)
The CTD electronic version, "electronic Common Technical Document (eCTD)," submitted by applicants to reviewers, was launched and became mandatory in 2016. This can be seen as a move to accelerate application and approval processes.
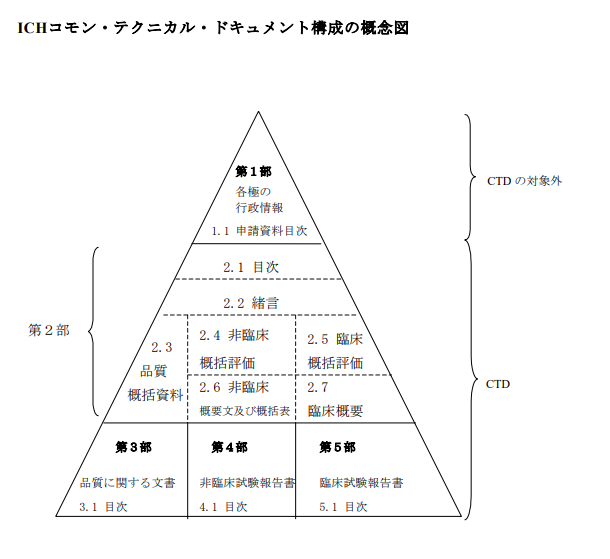
2. Structure of the CTD

CTD consists of five modules. Below is an introduction to their contents.
● Module 1: Information on Application Forms, Administrative Information, and Attached Documents
Information on application forms and other administrative documents, including region-specific documents.
●Module 2: Overview of the CTD
An outline concerning quality and clinical aspects. Includes the following seven items: Table of Contents, Introduction, Quality Overall Summary, Nonclinical Overview, Clinical Overview, Nonclinical Study Reports Summary and Tabular Listing, Clinical Summary.
● Module 3: Quality Information
Information related to the quality of pharmaceuticals, including manufacturing methods, ingredients, and quality testing of products. Chemical characteristics of the drug (drug structure, chemical properties, formulation information), manufacturing process of raw materials and products (raw materials, manufacturing methods, quality control methods), quality control and testing methods (stability testing, content verification testing, sterility testing, etc.), product stability data (long-term stability, temperature, humidity, storage condition information), batch records, and manufacturing processes are included.
● Module 4: Nonclinical Study Reports
A report summarizing the results of nonclinical studies (such as animal testing) conducted to evaluate whether the drug is safe for humans. It includes pharmacological tests (data on the biological effects of the drug), toxicity tests (acute toxicity, chronic toxicity, carcinogenicity, genotoxicity, effects on reproduction, etc.), pharmacokinetics (data on how the drug is absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted in the body), and safety assessments.
● Module 5: Clinical Trial Reports
A report summarizing the results of clinical trials (the effects of the drug on humans, safety, and efficacy). It includes an overview of the clinical trial (trial design, subjects, objectives), trial results (detailed data on efficacy and safety, comparison between treatment and control groups), adverse event data (frequency of drug-related adverse events, serious side effects, etc.), and conclusions and recommendations (conclusions based on the drug's efficacy and safety, recommendations for approval).
Module 5 is the section of the CTD that contains information related to clinical trials. It compiles detailed reports on clinical trials, including the Clinical Study Report (CSR).
Thus, the CTD is a document that systematically covers all necessary information from the early stages of drug development through clinical trials. It is important for streamlining drug development and accelerating applications and approvals in various countries and regions by using internationally standardized documents and formats in pharmaceutical submissions.
3. Cases Requiring CTD Translation and Important Points to Note in Translation

3-1. Cases Where CTD Translation Is Required
One case where CTD translation is required is when a Japanese pharmaceutical company applies to sell a new drug overseas. Documents generated from early development to clinical trials need to be translated, and since these are internationally standardized documents and formats, it enables efficient and rapid application and approval processes.
3-2. Important Points for CTD Translation
As with other clinical trial-related documents, the CTD contains important and sensitive information, so it goes without saying that utmost care is required to avoid any errors.
Furthermore, since the CTD covers a wide range beyond clinical trials, it includes detailed descriptions of drug quality, pharmacological data, drug interaction data, and manufacturing and quality control, making it more specialized.
4. Key Points for Efficient CTD Translation – Choosing the Right Medical Translation Company is Crucial

As a key point to efficiently advance CTD translation, we explain that selecting a medical translation company is crucial, and then introduce the selection criteria.
●Choose a translation company with experience in CTD, clinical trial documents, and pharmaceutical development-related translations
CTD is highly specialized and covers a wide range of fields. It is important to select a translation company with proven experience in clinical trial documents and pharmaceutical development, as well as translators with a track record in these areas.
●Choose a translation company that utilizes technology to provide highly efficient translation solutions
For the rapid development and sale of pharmaceuticals, it is necessary to quickly prepare and submit the CTD to authorities. You should select a translation company that can contribute to efficient CTD translation by leveraging machine translation, translation support tools, and AT.
5. Please also entrust CTD translation to Human Science
Human Science has extensive experience in translating clinical trial documents, including CTDs.
We also offer manual translation services and post-editing services. By utilizing translation support (CAT) tools such as Trados and machine translation tools, we strive to improve translation efficiency and quality, contributing to the further development of our clients.
Please try Human Science's medical translation, which combines high expertise in both document technology and medical science.
If you have any concerns or interests, please feel free to contact us.