Machine Translation Post-Editing: Points to Note & Examples of Work Using Dedicated Tools
>>Related Download Materials: 9 Examples of Machine Translation Errors and Post-Editing & Post-Editing Checklist
1. In some cases, post-editing can actually decrease work efficiency.
In general, post-editing work is considered to have a lower workload compared to translation work. Indeed, it is natural to think that making corrections based on machine-generated translations has a lower surface-level burden than translating from scratch.
However, in order to perform post-editing tasks accurately and quickly, a certain level of translation review (editing) skills is required. If there is insufficient appropriate experience, the workload may actually increase, and it may take longer compared to regular translation tasks.
Additionally, when providing formal post-editing services for corporations, it is important to clearly understand the differences between light editing and full editing, as not doing so may lead to increased workload.
2. Essential Steps in Post-Editing & Inadequacies of Free Machine Translation Tools
To reduce the workload of post-editing tasks, it is essential to improve translation review and post-editing skills, but at the same time, utilizing appropriate tools and features is also important.
For example, as one of the basic processes of post-editing, it is necessary to compare the results of multiple translation engines and select the one with the highest quality. However, typically free machine translation tools do not have the functionality to compare the results of multiple engines together. Therefore, it is necessary to open multiple engines in separate tabs from the browser and compare them individually.
Additionally, another fundamental process of post-editing is pre-editing. However, free machine translation tools typically lack features related to pre-editing, so everything must be done manually. Therefore, especially when dealing with a large volume, it can be inefficient and labor-intensive.
3. Example of Post-Editing Work Using Dedicated Tools ①
Therefore, this time we would like to see how much we can alleviate some of the burdens and issues mentioned above by using tools that have machine translation and post-editing assist features.
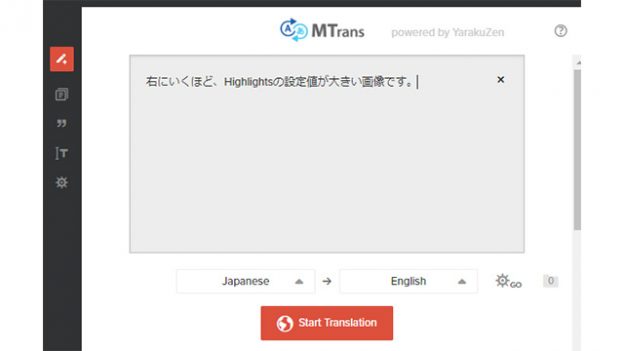
For this post-editing task, I would like to use the machine translation tool, MTrans. MTrans is compatible with CAT tools such as Trados and Memsource, but this time, I would like to use the standard browser version.
What is MTrans Team AI automatic translation software
1) First, enter the source text from the main screen of MTrans and press the "Start Translation" button.

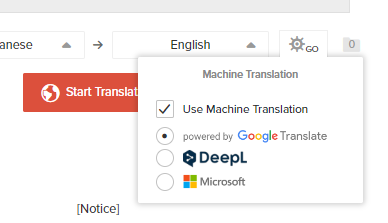
You can select the machine engine you want to use by pressing the " " located at the bottom right of the screen.
" located at the bottom right of the screen.
2) The results of the machine translation will be displayed, and the translated text will be confirmed through the following steps ① to ③.
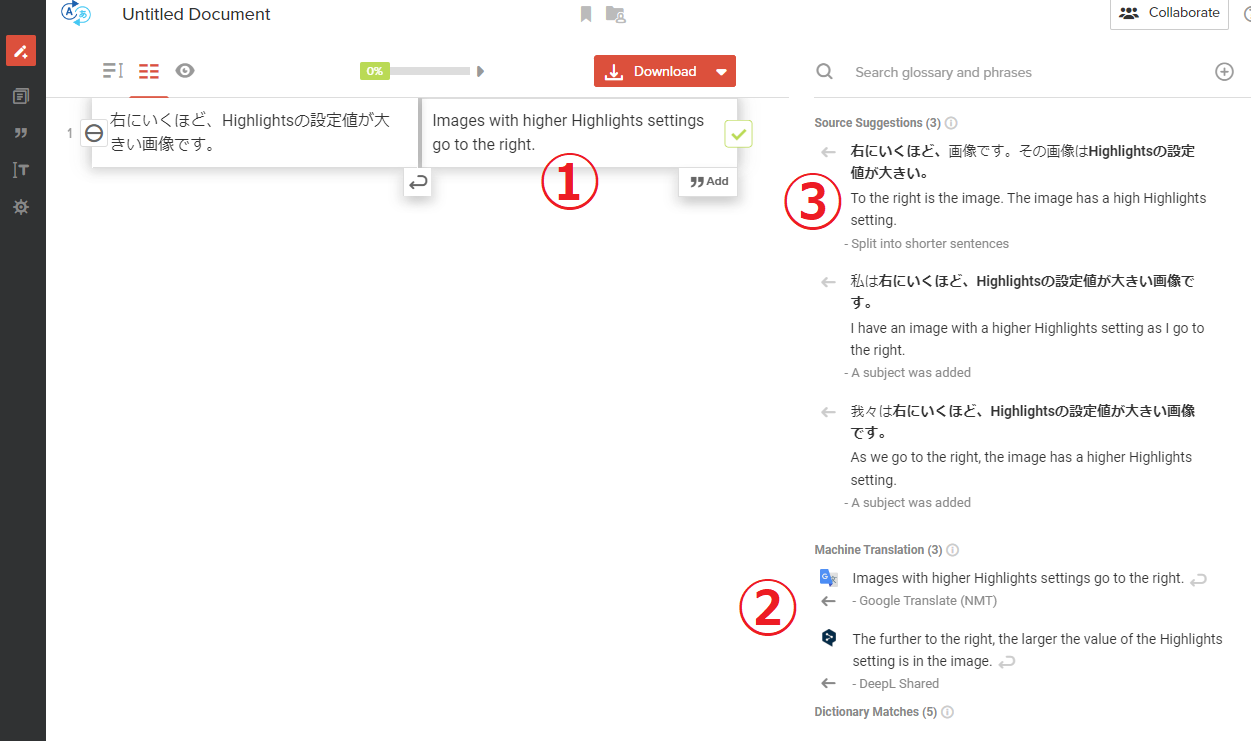
1. Check the quality of machine translation.
② Check the results of machine translation engines other than the selected one.
③ A revision proposal of the original text will be displayed, so if necessary, perform a pre-edit and run it through machine translation again.
3) After confirming ① to ③, we will determine which engine's results to use.
Below are the original text used in this example and the results displayed in response to it.
| Source | The image on the right has larger settings for Highlights. |
|---|---|
| Google Translate | Images with higher Highlights settings go to the right. |
| DeepL | The further to the right, the larger the value of the Highlights setting is in the image. |
This example shows Google Translate and DeepL.
Google Translate's "the further to the right" translates to "go to the right," which is nonsensical, and the structure also differs significantly from the original text due to paraphrasing. Therefore, I will use the results from DeepL, which align more closely with the original text in both structure and meaning.
4) We will perform post-editing (full editing).
| Source | The image on the right has larger settings for Highlights. |
|---|---|
| Post-edit | The |
As a point of post-editing, "the images to the right have larger highlight settings" means in context that "the further right the image is, the larger the highlight settings become," so it is necessary to appropriately revise the translation to reflect that expression.
Here is the post-edited translation.
| Source | The image on the right has larger settings for Highlights. |
|---|---|
| Translation | The closer the position of the image is to the right, the larger the value set for Highlights. |
4. Example of Post-Editing Work Using Dedicated Tools ②
I would like to introduce another example.
1) Enter the original text in the main screen of Mtrans and press "Start Translation".

2) Similar to Example 1 above, we will check the results of machine translation in the process (①~③).

3) Determine which engine's results to use. (Here, we only used Google Translate and DeepL as well.)
| Source | Select YES if you want to output the results later. Select NO if you do not want to output. |
|---|---|
| Google Translate | Select YES if you want to output the results later. Select NO for no output. |
| DeepL | Select YES if the results are to be output later. If no output is desired, select NO. |
Since the structure of the two sentences is not consistent, we will use the results from Google Translate this time.
4) We will perform post-editing (full editing).
| Source | Select YES if you want to output the results later. Select NO if you do not want to output. |
|---|---|
| Post-edit | Select YES Select NO |
The points for post-editing are as follows.
・In the expression "Select YES...", the phrase "if you want" was redundant and removed.
・In "Select NO...", the "results" that are subject to "not outputting" are omitted, so it should be appropriately reflected (Note: This sentence is indefinite, so the pronoun "you" is used)
Here is the post-edited translation.
| Source | Select YES if you want to output the results later. Select NO if you do not want to output. |
|---|---|
| Translation | Select YES to output the results later. Select NO if you do not wish to output any results. |
5. Summary
In this way, it is recommended to use dedicated tools to more efficiently compare the results of two or more engines and perform pre-editing tasks during post-editing. Additionally, it is important to be aware of security issues, as free machine translation engines may expose the input data to third parties and use it for the engine's learning purposes.