As machine translation becomes more widespread, the demand for post-editing is also increasing. However, due to the differences in workflow compared to human translation, it is often avoided by translators.
However, by correctly understanding the differences between human translation and post-editing, and by automating some aspects of the post-editing process, it is possible to streamline post-editing tasks and reduce the burden on translators.
Table of Contents
1. The Difference Between Human Translation and Post-Editing
2. Reasons Why Translators Dislike Post-Editing
3. Post-editing can be automated
1. The Difference Between Human Translation and Post-Editing
Post-editing is primarily handled by translators who have experience in human translation, but the workflow differs from that of human translation.
What exactly is different?
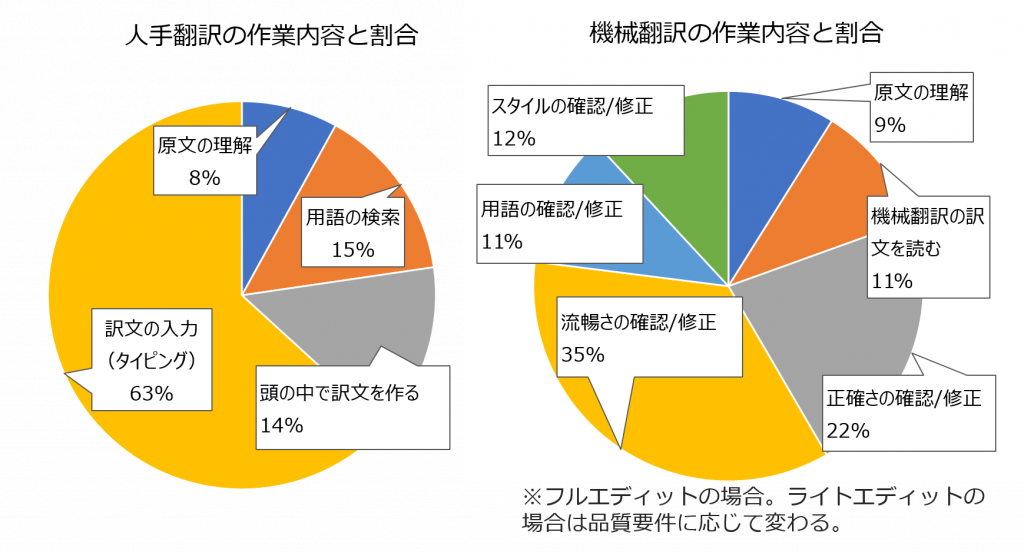
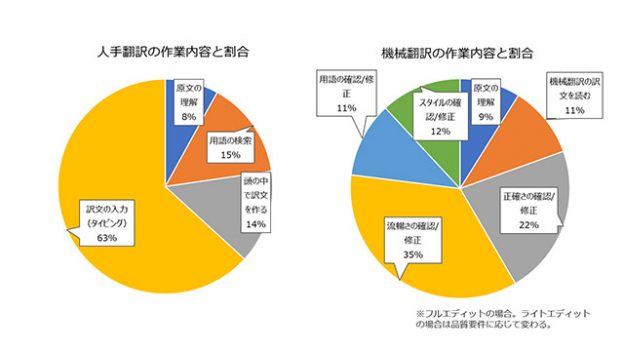
In human translation, 63% of the work consists of inputting (typing) the translated text.
In contrast, in post-editing, 35% is for "fluency checks/corrections" and 22% is for "accuracy checks/corrections."
It requires different know-how compared to human translation.
2. Reasons Why Translators Dislike Post-Editing and Characteristics of Machine Translated Text
Many translators seem to feel resistance to mastering post-editing work because the workflow differs significantly from human translation.
Moreover, the unit price for post-editing is lower than that of human translation, which raises the psychological barrier even further.
The tedious tasks of correcting terminology and style also contribute to translators avoiding post-editing.
To promote machine translation, it is necessary for the translation departments of client companies and translation agencies to provide support that alleviates the burden on translators.
What are the challenges of post-editing? Generally, the following issues are cited as problems with machine-translated texts.
- ・Translation is done on a sentence-by-sentence basis. It cannot be translated with expressions or terms that fit the context.
- ・There may be mistakes in the dependency structure.
- ・Terminology/Style is not consistent
- Service name in English/Japanese is inconsistent
- Inconsistent full-width/half-width alphanumeric characters and symbols
- Cannot insert spaces between full-width and half-width characters
- Inconsistent long vowels at the end of katakana words, etc.
- Style: The colon is in half-width. Unnecessary spaces have been removed.
- Term: The translated terms from the glossary are used.
If we can streamline even some of these machine translation errors, it may reduce the burden on translators.
3. Post-editing can be automated
What can be done on the requester side of post-editing to improve the translator's work efficiency?
There are three main points.
①Clarification of Quality Requirements
Let's agree on the quality requirements with the client and share them with the translator.
②Improvement of Accuracy and Fluency
Machine translation engines are updated daily. Regularly compare multiple engines and use the best one.
③Automatic Correction of Terminology and Style
Let's automate what can be automated during post-editing tasks.
Utilizing the engine's terminology and style features is also an effective measure.
Here, we introduce MTrans for Memsource/Trados, which automates terminology and style processing on Memsource/Trados.
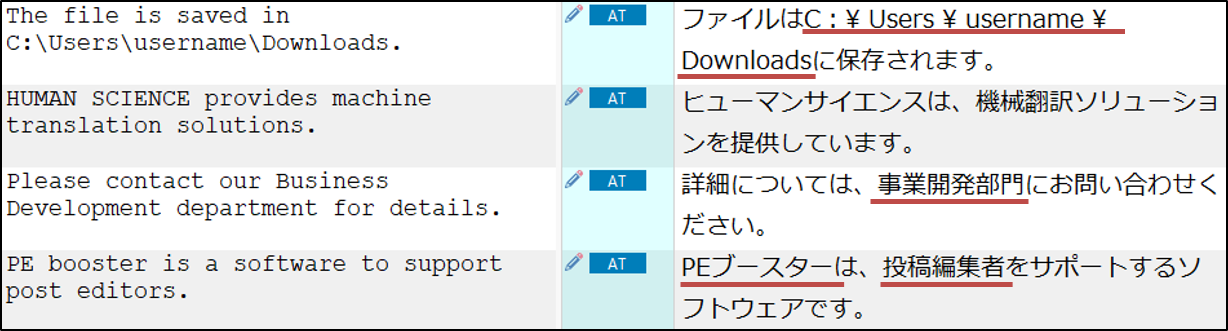
This is a text that has been translated using Google Translate.
Style: The colons are full-width. There are unnecessary spaces.
Terminology: Different translations from the glossary are being used.
Both style and terminology need to be corrected through post-editing.
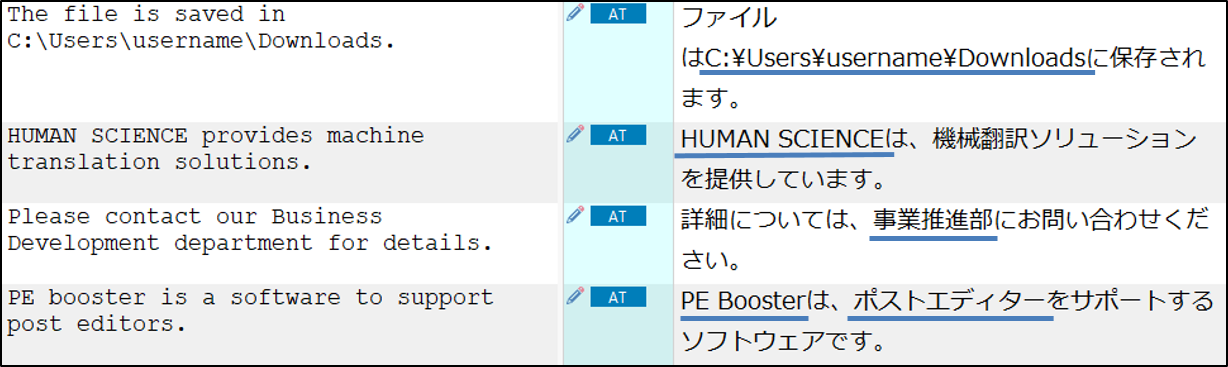
This is the machine translation processed with the automatic post-editing feature of MTrans.
Terminology and style are applied automatically.
To what extent has the workload been reduced through automatic processing of styles and terminology?
Let's take a look at the amount of corrections and time for 109 sentences.
| MTrans | ||
|---|---|---|
| Correction Rate | 87% (95/109 sentences) | 0% (0/109 sentences) |
| Number of Corrections | 661 | 0 |
| Correction Time | 25 minutes 5 seconds | 0 seconds |
| Quality of Translation | Good (The translator could not focus on accuracy/fluency) |
Excellent (The translator was able to focus on accuracy/fluidity) |
In the case of Google, 87% of the 109 sentences required corrections, while MTrans had zero.
There was also a difference of 25 minutes in correction time.
Not only was the working time reduced, but the quality of the translation improved as the translators could focus on accuracy and fluency checks.
4. Summary
In this way, if there are style and terminology automation tools available, actively utilizing them can lead not only to increased efficiency but also to improved quality.
MTrans for Memsource/Trados is a machine translation solution developed by our company for corporate clients. By implementing MTrans, you can utilize machine translations from Google/DeepL/Microsoft. There is no need to contract with each company providing machine translation services. Additionally, it is equipped with necessary features for industrial translation, such as automatic application of terminology and style rules, significantly reducing post-editing work.
For more details, please see here.
MTrans for Trados
MTrans for Memsource