The accuracy of machine translation is improving day by day, but its quality still requires human intervention. One of the major reasons is that machine translation can only process the original text on a sentence-by-sentence basis, and it cannot take into account omitted subjects, objects, or the surrounding context and nuances. In other words, even if there are words omitted in the original text for readability or conciseness, machine translation can only process what is written in the original text, leading to a higher likelihood of unnatural translations or mistranslations.
In this blog, we will introduce how to improve the efficiency of post-editing work through pre-editing (the process of rewriting the original text to make it easier for machine translation), while providing examples of cases where some content is omitted in the original text.
- Table of Contents
1. Example 1: Cases where the subject is omitted
- ●Original text: This will be cleared by the following operation.
- ●Machine Translation: It will be cleared by the following operation.
- ⇓
- ●Pre-edit: The value will be cleared by the following operation.
- ●Machine Translation: The value is cleared by the following operation.
- ⇓
- ●After correction: The values are cleared by the following operations.
In this example, the subject "value" is omitted, so the machine translation uses "It" as the subject. Therefore, if we add "The value" to the original text and process it again with machine translation, it will correctly reflect "The value" as the subject.
However, when only the subject is usually omitted, it is often sufficient to replace pronouns like "It" with the appropriate subject during post-editing, so in some cases, pre-editing may not be necessary.
* Since the context involves multiple values and operations, "value is" has been corrected to "values are" and "operation" to "operations." Machine translation tends to struggle with recognizing singular and plural forms in nouns present in the original Japanese text, so caution is advised.
2. Example ②: Cases where the object is omitted
- ●Original: The ability to change the display time for each user.
- ●Machine Translation: The time until display can be changed for each user.
- ⇓
- ●Pre-edit: The ability to change the display time of the control bar for each user.
- ●Machine Translation: The time to display the control bar can be changed for each user.
- ⇓
- ●After modification: The time by which to display the control bar can be changed for each user.
In this example, since the target of "until display" is omitted, changing it to the more accurate expression "to display the control bar" as the object of "time" will improve the results of machine translation. Saying "The time until display" may confuse users.
* If you want to emphasize "for each user," it is also possible to say, "For each user, the time..."
3. Example ③: Cases where some content is omitted
- ●Source: Please slide the DATA switch horizontally one at a time.
- ●Machine Translation: Slide the DATA switches horizontally one by one.
- ⇓
- ●Pre-edit: Slide the DATA switch horizontally one by one using a flathead screwdriver.
- ●Machine Translation: Slide the DATA switches horizontally one by one using a flat-blade screwdriver.
- ⇓
- ●After modification: Slide the DATA switches one by one in a horizontal direction using a flathead screwdriver.
In this example, since "using a screwdriver" has been omitted (due to being mentioned earlier), it is necessary to reflect that content in the original text.
In the instruction manual, there may be instances where repeated content is omitted, so caution is required.
4. Example ④: Cases where multiple contents are omitted
- ●Original: If not set, please add and open the file name from the teacher's editing, or have the student resubmit it.
- ●Machine Translation: If it is not set, please add it from the file name edited by the teacher and open it, or let the student resubmit it.
- ⇓
- ●Pre-edit: If the file extension is not set, please have the teacher add the extension from the field for editing the file name before opening the file, or have the student set the appropriate extension in the file name and resubmit it.
- ●Machine Translation: If the extension is not set, the teacher should either add the extension from the Edit File Name field before opening the file, or have the student resubmit the file with the appropriate extension set to the file name.
- ⇓
- ●After correction: If the extension is not set, the teacher should add it from the field in which to the edit file name before opening the file, or have the student resubmit the file with a proper extension set to the file name.
The original text here omits a lot of information, making the result of machine translation nearly incomprehensible. In such cases, it is necessary to completely rewrite the original text according to the context and reprocess it with machine translation.
Additionally, pre-editing can be done in real-time on the machine translation screen, allowing for efficient progress in work. Below is a screen where pre-editing was performed using the example of "4". (Tool used: Our company's AI-powered automatic translation tool MTrans Team)
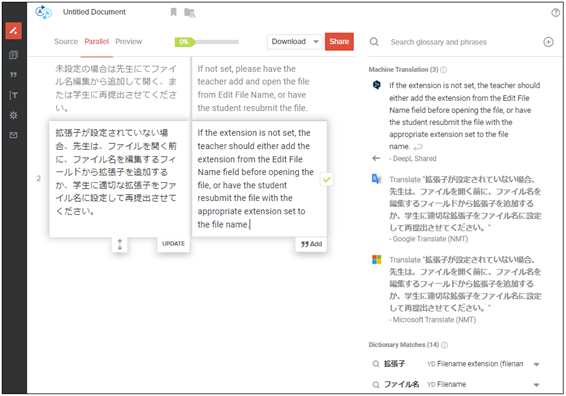
Machine translation is evolving daily, but due to various omissions in the original text (which are often seen in Japanese), there are many cases where quality issues arise. Therefore, performing pre-editing in real-time while simultaneously conducting post-editing is an important point for the future utilization of machine translation.