The text generation AI ChatGPT is gaining attention. When given a theme, it can generate text based on that theme in natural language, and it can also support programming, marking the arrival of a highly advanced AI. However, such AIs learn from text data and code that already exist on the internet, so in specific fields that require high levels of expertise and confidentiality, such as medical records, there may not be enough information for the AI to learn from. To solve problems in these fields using AI, it is still necessary to incorporate various forms of tacit knowledge, such as human experience, wisdom, and intuition, into algorithms. Therefore, human annotation work is still required in many situations.
Annotation tools are indispensable for the annotation work that involves adding information to each piece of large amounts of data. However, when you search for terms like "annotation tool," various names appear, each supporting different file formats and functions, making it confusing to decide which tool to use. Therefore, this time, we will focus specifically on text annotation and introduce three points to consider when choosing an annotation tool, along with four recommended annotation tools.
- Table of Contents
-
- 1. Three Points to Choose an Annotation Tool
- 1-1. Purpose
- 1-2. Features and Usability
- 1-3. Management
- 2. Comparison of 4 Annotation Tools
- 2-1. FastLabel
- 2-2. Brat
- 2-3. LabelBox
- 2-4. Label Studio
- 3. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- 4. Summary
- 5. Human Science Annotation Agency Services
- 5-1. Extensive track record of creating 48 million teacher data entries
- 5-2. Resource management without crowdsourcing
- 5-3. The latest data annotation tools
- 5-4. Secure room in office
- 5-5. In-house Production Support
1. Three Points to Choose an Annotation Tool
There are many text annotation tools, and it is often difficult to understand "which one ultimately suits your company" just by comparing features and prices.
To proceed smoothly with tool selection, it is important to organize and consider the following three perspectives in order.
・What is the purpose of performing annotation?
・What functions and ease of use are necessary for the task?
・What kind of system will be used for management and operation?
By clarifying these points in advance, the differences between cloud-based and local types, as well as the suitability of commercial tools versus OSS tools, will naturally become clear. Below, we will sequentially explain the three key points to keep in mind when selecting a text annotation tool.
1-1. Purpose
Text annotation tools need to be selected based on the type of AI model you want to build in-house. Typical types of text annotation include "named entity recognition," "sentiment analysis," and "class classification," but the optimal annotation tool varies for each. For example, for "named entity recognition," a feature that allows specific words in a sentence to be enclosed in span tags is necessary. For "sentiment analysis" using dialogue, it would be beneficial to have tagging for each sentence. In "class classification," which categorizes the entire text, a tagging function for the whole text is required. Since the types of annotations that can be performed vary by tool, choose a tool that fits your purpose.
1-2. Features and Usability
In annotation work that processes vast amounts of data, the functionality and usability (operability) of the tools are crucial. From the perspective of operability, it is important for the UI (button arrangement and screen layout) to be intuitive enough to operate without a manual, whether shortcut keys are well-equipped, and whether actions like data loading are smooth, as these factors contribute to productivity improvement. In terms of functionality, it is advisable to consider whether the tool can create the necessary data for AI learning, such as the ability to associate span tags with each other.
Additionally, annotation tools are broadly divided into cloud-based and local installation types. Cloud-based tools require no installation and can be used immediately after creating an account and logging in.
On the other hand, local types can operate without transferring data to external cloud servers, providing peace of mind in terms of data security management. Some tools have a high barrier to entry, requiring downloads from version control systems like GitHub or executing commands for installation. Additionally, many tools lack features for bulk data management, making data management cumbersome and not very suitable for collaborative work.
Furthermore, the data formats that can be output by each tool vary. Whether the desired output format is supported is also one of the important points to consider when choosing a tool.
1-3. Management
When working with many annotators on a single project, the management functions for annotators and tasks (the smallest unit of annotation work) are also crucial points not to be overlooked. For example, being able to check the daily progress of annotators (number of annotations, number of completed tasks, number of rejections, etc.) and the status of each task (annotated, reviewed, under review, on hold, etc.) can facilitate smooth management operations and also help ensure quality.
Most local tools lack such management features, but many cloud tools come equipped with management functions, making them effective for projects involving large amounts of data carried out by multiple people over an extended period.
2. Comparison of 4 Text Annotation Tools
This time, we will introduce four representative annotation tools in the field of text annotation.
Comparison Table of Major Text Annotation Tools
2-1. FastLabel (Free/Paid)
FastLabel is a cloud-based annotation tool that supports images, videos, text, audio, 3D, and automatic annotation.
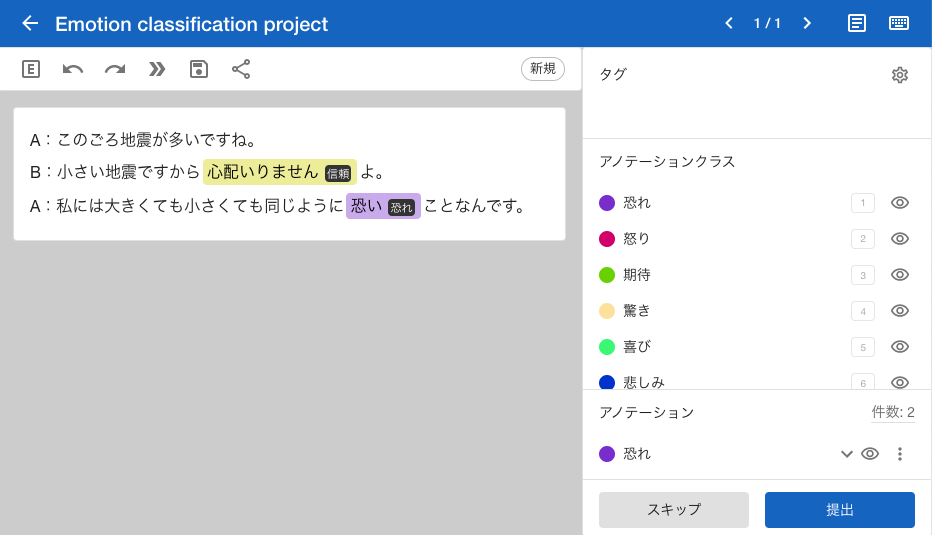
FastLabel's text annotation supports "Named Entity Recognition", "Classification", and "Pair Classification".
"Named Entity Recognition" is an annotation that extracts specified words or sentences from the text. "Classification" allows you to categorize the entire text as a whole into specified types. Additionally, "Pair Classification" enables you to compare and classify two texts side by side.
In addition, FastLabel operates smoothly, always displaying quickly when loading pages or navigating between menus. It also supports auto-annotation, which can reduce manual labor costs. Furthermore, it has project management features that allow for tracking work progress and reviewing data all within the tool.
For information about FastLabel, click here.
2-2. brat (Free)
BRAT stands for "BRAT Rapid Annotation Tool" and is an open-source, locally installed tool used in browsers. It allows for the extraction of named entities from text and their associations. By linking proper nouns to sources like Wikipedia, it is also possible to normalize nouns. Multiple users can access the annotation data and work simultaneously.
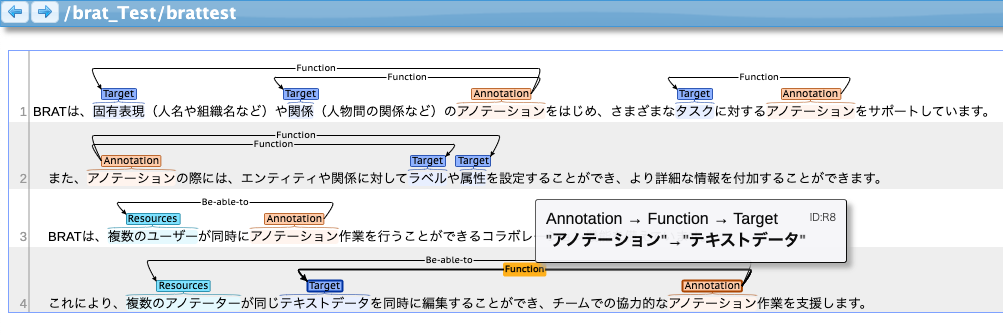
To use this, Python 2 is required, and installation is done by entering commands in the terminal or similar. Settings for classification labels cannot be done within the tool; instead, you need to write directly into the label configuration files provided in the installed brat directory. Additionally, you must create a file in advance to export the annotation data. Information about these installations and necessary settings is only briefly explained on the homepage, so the barrier from installation to the start of annotation work can be considered somewhat high. Furthermore, there are no project management features such as review functions or progress/status tracking, so when advancing a project with multiple people, it is necessary to establish an appropriate management plan to compensate for this.
There are many external forums about projects using this tool, where you can refer to various projects. It can be said to be optimal for annotation work as academic research.
For information about brat, click here.
2-3. LabelBox (Free/Paid)
LabelBox is a cloud-based annotation tool. It supports various annotations for images, videos, text, DICOM-compliant medical data, and map data such as COG. The paid version offers a wealth of features, while the free version is positioned as a trial version with limited functionality. The text annotation in the free version supports classification on a sentence-by-sentence basis. It can be used for sentiment analysis of dialogue, among other applications.
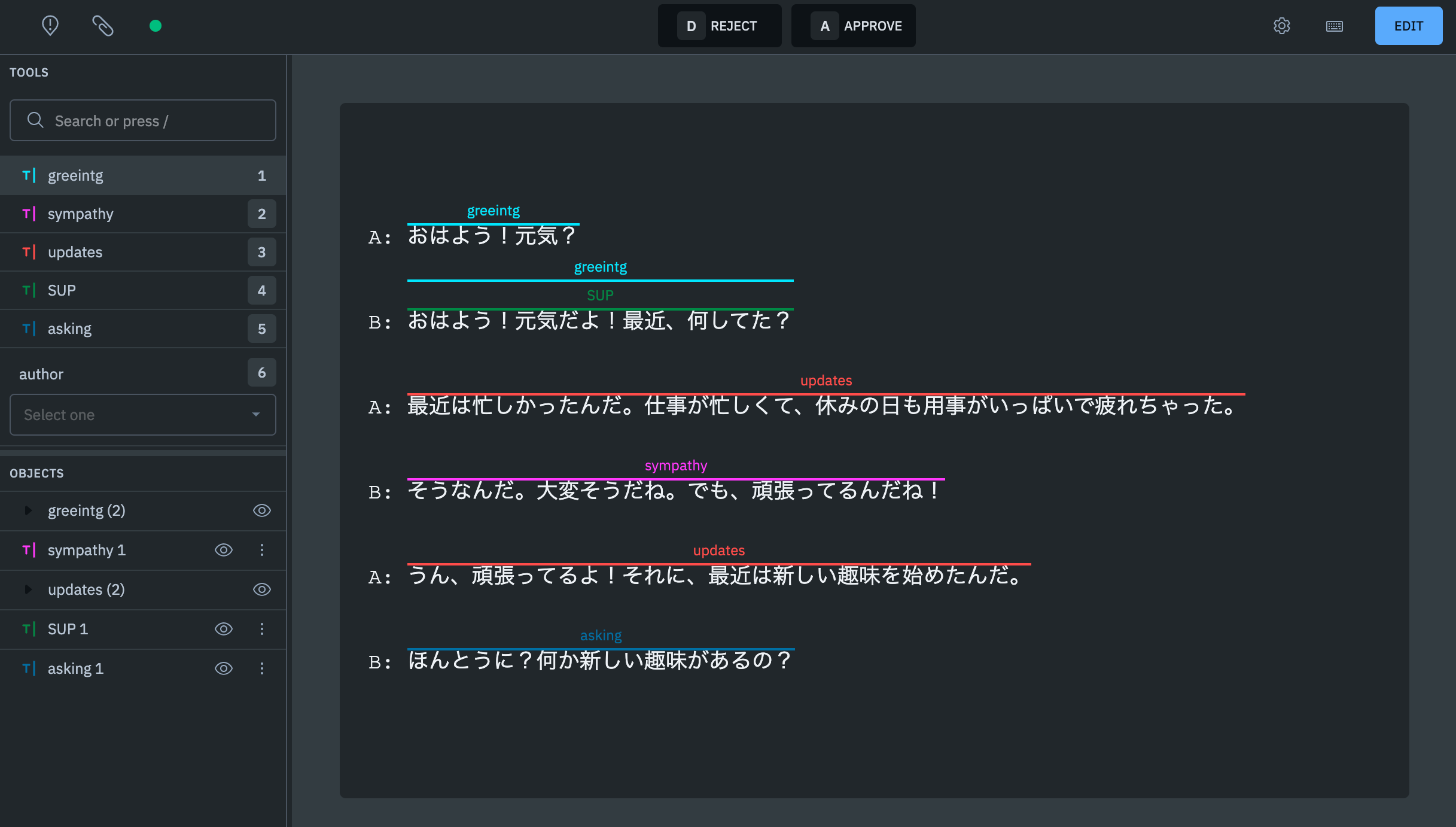
The paid version supports various text annotations such as named entity extraction and text classification. Additionally, if you use already annotated data, auto-annotation is also possible. It also includes management features for reviews and progress tracking, making it suitable for large-scale projects or ongoing projects.
For information about LabelBox, click here.
2-4. Label Studio (Free/Paid)
Label Studio is an open-source annotation tool boasting high flexibility. It supports various data formats such as images, audio, and text, and allows you to build custom labeling UIs. It can be easily deployed in local environments or on-premises, making it suitable for handling highly confidential medical data and internal company data. It is widely used by major corporations and research institutions, and is recommended for users who prioritize extensibility and customization.
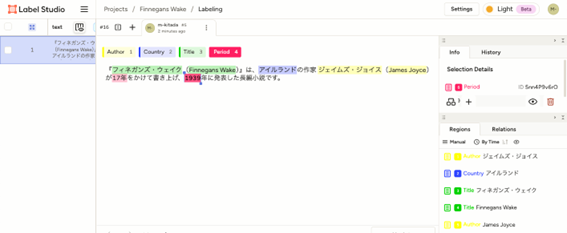
For information about Label Studio, click here.
3. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q. How much does the implementation cost?
A. You can start with zero initial cost by using open-source or free tools, but commercial tools generally use a monthly subscription or pay-as-you-go pricing. Since costs vary greatly depending on the team size and required features, we recommend testing with trials or free plans.
Q. Can security requirements be met?
A. When handling highly confidential data such as contracts, medical records, and patented technology documents, choose tools that allow on-premises operation, data encryption, and access control. With open-source tools like Label Studio, it is also possible to build a local environment, which helps prevent the leakage of confidential information.
Q. Does it support Japanese?
A. Fast Label is developed by a Japanese company, so manuals and other materials are available in Japanese. For other tools, all information is only in English. However, all data supports Japanese text, so you can work with Japanese text files.
Q. Can annotation quality be guaranteed by the tool alone?
A. Tools are means to improve work efficiency and do not guarantee quality itself. The overall design of the operational process—including annotation design (label definitions and judgment criteria), review systems, and rejection rules—affects quality. For large-scale projects or when high accuracy is required, a review system by a specialized team is important.
Q. Can it also be used for data creation for generative AI and LLMs?
A. Yes, it can be used not only for classification and named entity extraction but also for creating instruction-following data, which is manually organized to specify what kind of questions should receive what kind of answers. For generative AI applications, designing the granularity and structure of the answers is more important than just labeling, so considering data design alongside tool selection is essential.
Q. Which should I choose, tool implementation or annotation outsourcing?
A. If you have sufficient internal resources and annotation expertise, implementing a suitable tool may be appropriate. If short-term, high-quality, and large-scale support is required, outsourcing services are more suitable.
There is also a hybrid approach that combines tool implementation and annotation outsourcing, where only the design and initial setup are outsourced externally. It is advisable to proceed while consulting with the outsourcing service company according to the development scale.
4. Summary
This time, we explained three key points to consider when choosing annotation tools and introduced four recommended text annotation tools.
As the number of annotation tools has increased recently, it is important to choose and utilize the most suitable annotation tool for your company's purposes in order to streamline the time-consuming annotation tasks as much as possible.
If you want to reduce the cost of implementing annotation tools, considering outsourcing the annotation itself is also an effective option. Our company offers a wide range of services from consultation on annotation tools to the outsourcing of annotation, so please feel free to reach out to us.
5. Human Science Training Data Creation, LLM RAG Data Structuring Outsourcing Service
5-1. Extensive track record of creating 48 million teacher data entries
At Human Science, we are involved in AI model development projects across various industries, starting with natural language processing, including medical support, automotive, IT, manufacturing, and construction. Through direct transactions with many companies, including GAFAM, we have provided over 48 million high-quality training data. We handle a wide range of training data creation, data labeling, and data structuring, from small-scale projects to long-term large projects with a team of 150 annotators, regardless of the industry.
5-2. Resource management without crowdsourcing
At Human Science, we do not use crowdsourcing. Instead, projects are handled by personnel who are contracted with us directly. Based on a solid understanding of each member's practical experience and their evaluations from previous projects, we form teams that can deliver maximum performance.
5-3. Support for Not Only Creating Training Data but Also Creating and Structuring Generative AI LLM Datasets
We support not only labeling for data organization and the creation of training data for identification-type AI, but also the structuring of document data for generative AI and LLM RAG construction. Since our founding, manual production has been a core business and service, and currently, we also assist in creating documents that AI can easily recognize to facilitate the introduction of generative AI for corporate knowledge utilization. In sharing and leveraging corporate knowledge and documents using generative AI, current technology still cannot achieve 100% accuracy with tools alone. For customers who want to make the most of their past document assets, we also provide document data structuring. We offer optimal solutions leveraging our unique expertise, deeply familiar with various types of documents.
5-4. Secure room in office
Within our Shinjuku office at Human Science, we have secure rooms that meet ISMS standards. Therefore, we can guarantee security, even for projects that include highly confidential data. We consider the preservation of confidentiality to be extremely important for all projects. When working remotely as well, our information security management system has received high praise from clients, because not only do we implement hardware measures, we continuously provide security training to our personnel.
5-5. In-house Production Support
We provide staffing services for annotation-experienced personnel and project managers tailored to your tasks and situation. It is also possible to organize a team stationed at your site. Additionally, we support the training of your operators and project managers, assist in selecting tools suited to your circumstances, and help build optimal processes such as automation and work methods to improve quality and productivity. We are here to support your challenges related to annotation and data labeling.

 Text Annotation
Text Annotation Audio Annotation
Audio Annotation Image & Video Annotation
Image & Video Annotation Generative AI, LLM, RAG Data Structuring
Generative AI, LLM, RAG Data Structuring
 AI Model Development
AI Model Development In-House Support
In-House Support For the medical industry
For the medical industry For the automotive industry
For the automotive industry For the IT industry
For the IT industry For the manufacturing industry
For the manufacturing industry