As a method for business improvement and streamlining, RPA is often seen alongside AI.
In this article,
"What is RPA?"
"What is the difference from AI?"
"What are the possible uses?"
We will explain the basic usage of RPA and the differences from AI for those who are unfamiliar. We will also introduce examples of utilizing RPA and AI together.
- Table of Contents
-
- 1. Differences between RPA and AI
- 1-1. What is RPA?
- 1-2. What is AI?
- 1-3. Differences between RPA and AI
- 1-4. Background of RPA's Attention
- 1-5. Benefits of RPA Implementation
- 2. Types of RPA Tools
- 2-1. Desktop Type (On-Premises)
- 2-2. Server Type (On-Premises)
- 2-3. Cloud-based
- 3. Utilization of RPA
- 3-1. Input and Transcription of Data and Text
- 3-2. Comparison and Verification of Information
- 3-3. Monitoring
- 4. Three Classes of RPA
- 4-1. Class 1: RPA (Robotic Process Automation)
- 4-2. Class 2: EPA (Enhanced Process Automation)
- 4-3. Class 3: CA (Cognitive Automation)
- 5. Future Evolution
- 5-1. Recommended Tools
- 6. Examples of Utilizing RPA and AI in Collaboration
- 6-1. Digitization of Paper Materials in Local Governments
- 6-2. Combination of AI-based decision making and RPA-based routine tasks
- 7. For inquiries about utilizing AI, please contact Human Science Co., Ltd.
- 7-1. 48 million records of teacher data creation
- 7-2. Resource Management without Using Crowdsourcing
- 7-3. Utilizing the Latest Data Annotation Tools
- 7-4. Equipped with a security room within the company
1. Differences between RPA and AI

We will look at the differences between RPA and AI from their respective overviews.
1-1. What is RPA?
RPA stands for Robotic Process Automation. It refers to the automation of tasks by robots. The tasks in question are routine tasks such as data input and transcription, file duplication and movement, performed on a computer. The robot executes the same actions as a human on the screen. To run RPA, it is necessary to first specify the tasks that the human wants the robot to perform and record them with RPA.
1-2. What is AI?
AI stands for Artificial Intelligence. It refers to the actual artificial intelligence itself. AI can make decisions on its own for given tasks. Pre-training machine learning is necessary to operate AI. By providing training data called "teacher data", AI can learn features and patterns from it and acquire decision-making abilities.
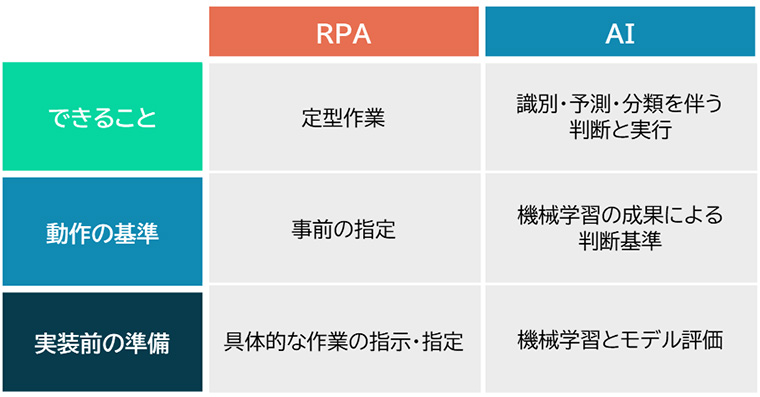
1-3. Differences between RPA and AI
The decisive difference between RPA and AI is whether the system itself can make judgments. RPA only executes what humans have specified. It cannot do anything more. On the other hand, AI can execute tasks based on pre-learning and its own judgment.
Please also refer to this article for information on AI machine learning and training data.
>>What is training data? Explanation from the relationship with AI, machine learning, and annotation to how to create it.
1-4. Background of RPA's Attention
The reason why RPA is attracting attention is due to "solving the shortage of human resources" and "improving work efficiency". Japan is facing a declining working population due to its aging population, and the decrease in labor force is becoming a social issue in various industries. In particular, the shortage of human resources in the IT industry is a serious problem.
According to the "Survey on IT Human Resources Demand and Supply" announced by the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry in March 2019, it is said that up to approximately 790,000 IT personnel will be in shortage by 2030. By assigning some tasks to RPA, the effective use of human resources has become more conscious. RPA is attracting attention as a tool that can solve the chronic shortage of human resources and achieve business efficiency.
1-5. Benefits of RPA Implementation
RPA can delegate tasks that have been done by humans, resulting in improved efficiency. Many RPA systems can be configured through simple operations such as drag and drop, eliminating the need for advanced programming knowledge. This ease of implementation is believed to greatly reduce the time and effort required for training and development.
By automating existing tasks, you can utilize the extra time to focus on creative tasks such as sales and planning. RPA is suitable for automating mechanical tasks, but recently, there are also versions equipped with AI.
2. Types of RPA Tools

There are three main types of tools for implementing RPA.
2-1. Desktop Type (On-Premises)
This is a method for installing tools on each machine that you want to use RPA with. It is suitable for those who want to start small and keep initial costs low.
2-2. Server Type (On-Premises)
This is a method for installing RPA tools on servers and user machines on-premises. You can manage the tools for each machine on the server side. Large-scale operations are also possible.
2-3. Cloud-based
This is a method for using an RPA system installed on the provider's server online. It can also support remote operation while keeping costs down.
3. Utilization of RPA

RPA is capable of simple tasks and routine work. Processing tasks and repetitive work according to established rules are RPA's areas of expertise. Here are some typical use cases.
3-1. Input and Transcription of Data and Text
You can automatically input data and text in browsers and spreadsheets. It is also possible to transfer data from a browser to a spreadsheet and cross tools. It is possible to process quickly without worrying about transcription errors.
Example: Transfer the contents of an inquiry form to a spreadsheet.
3-2. Comparison and Verification of Information
You can collect information from multiple applications and compare and match their contents. Here are some examples:
Example: Automatically generate aggregated reports on a regular basis.
3-3. Monitoring
You can monitor the status of systems and other things. This reduces the workload of human checks and leads to prompt response in case of abnormalities.
Example: Monitor system data and send an email to the responsible person if there is any unusual activity.
4. Three Classes of RPA

There are three classes in RPA.
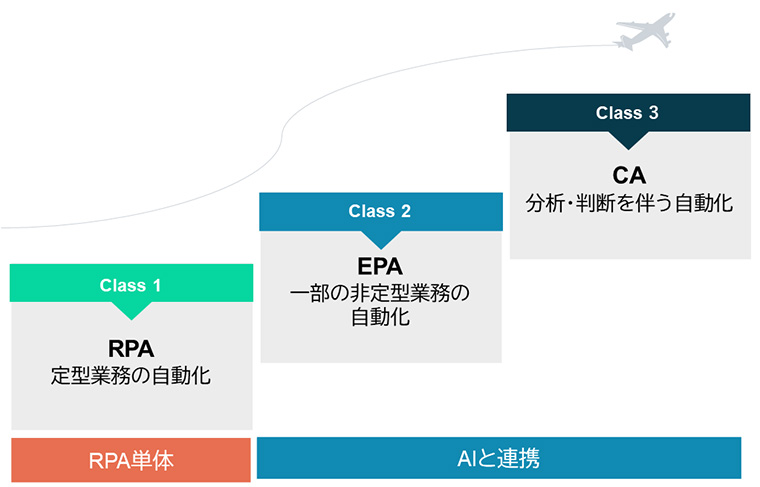
4-1. Class 1: RPA (Robotic Process Automation)
The above explains the conventional type of RPA, which falls under this class 1. It is capable of automating routine tasks. It is difficult to handle exceptional situations.
4-2. Class 2: EPA (Enhanced Process Automation)
By collaborating with AI, we can handle non-routine tasks to a certain extent. We can also handle some exceptional situations.
4-3. Class 3: CA (Cognitive Automation)
Higher level of automation. With advanced AI integration, it is possible for robots to analyze data and construct task-specific workflows on their own.
5. Evolution through RPA Implementation
Tasks such as creating invoices and customer lists, which involve simply transcribing information, can be delegated to RPA. In the future, the variety of RPA will increase and its range of applications will expand. After implementing RPA, labor costs will be significantly reduced, allowing for the allocation of resources and time towards creative activities that cannot be automated, as mentioned earlier.
However, tasks such as reading text from handwritten images are difficult for RPA, and AI technology is necessary for automation. In the future, RPA equipped with AI (artificial intelligence) is expected to become more widespread. By combining AI technology, tasks that were previously difficult to automate with traditional RPA will also be automated.
5-1. Recommended RPA Tools
Introducing recommended RPA tools for utilizing RPA in business.
1. Automation 360 | Automation Anywhere (Hitachi Solutions)
"Automation 360" is the latest RPA platform provided by Automation Anywhere, sold by Hitachi Solutions, and supported by user technical support. It has both cloud-based and on-premises options, and the ability to use it in a browser makes it attractive as it can be introduced without major changes to the company's environment.
Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud are certified for hosting, providing scalability that can grow with your company's growth. The system incorporates AI technology, making it possible to automate tasks regardless of the user's skill level.
The learning service "Automation Anywhere University" is available, allowing you to learn about development and operation through various video content.
>>RPA Business Automation Solution Automation 360
WinActor | NTT Business Solutions
"WinActor" is an RPA solution provided by NTT Advanced Technology. It has gained attention as a domestically developed RPA tool within the NTT Group.
It is possible to create scenarios for automation realization through drag-and-drop operations. It is compatible with all software that can be operated from Windows terminals, such as email, browsers, and Microsoft Office products, making it possible to achieve business efficiency.
Report creation, web research, communication, transcription work, etc. can all be automated for any job or department.
6. Examples of Utilizing RPA and AI in Collaboration

By combining the strengths of RPA and AI, it is possible to achieve greater business efficiency than by implementing them separately. Here are some examples of how AI and RPA can be used together.
6-1. Digitization of Paper Materials in Local Governments
In one local government, when registering the contents of paper materials into the system, it was previously processed by visually confirming and manually inputting by staff. During peak periods of concentrated applications such as tax declarations and moving notifications, staff would become completely occupied with this task, so it was decided to verify the effectiveness of business improvement through automation.
・Methods of Automation
Automate text information reading with AI OCR. Extract text areas from scanned document images using AI OCR, and convert the content, including handwritten characters, into data that can be used on a computer. Then, RPA automatically transfers and registers the data into the system.
・Effect
Based on the verification results, it was found that this automation can reduce the workload by 1,400 hours per year.
>>Verified business automation using AI-OCR and RPA
6-2. Combination of AI-based decision making and RPA-based routine tasks
With the AI OCR introduced in this case, even difficult handwritten characters can be predicted and judged by AI. The surrounding characters and pre-learned data serve as the criteria for this judgment. By combining this unique prediction and judgment process with the high-speed automatic input of RPA, significant business efficiency can be achieved.
7. For inquiries about utilizing AI, please contact Human Science Co., Ltd.
7-1. 48 million records of teacher data creation
"I don't know where to start when it comes to implementing AI."
"I don't know what to ask for when outsourcing."
If you are in such a situation, please consult with Human Science. At Human Science, we participate in AI development projects in various industries such as natural language processing, medical support, automobiles, IT, manufacturing, and construction. Through direct transactions with many companies including GAFAM, we have provided over 48 million high-quality training data. We can handle various annotation projects regardless of industry, from small-scale projects to large-scale projects with 150 annotators.
>>Human Science's Annotation Service
7-2. Resource Management without Using Crowdsourcing
At Human Science, we do not use crowdsourcing and instead directly contract with workers to manage projects. We carefully assess each member's practical experience and evaluations from previous projects to form a team that can perform to the best of their abilities.
7-3. Utilizing the Latest Data Annotation Tools
One of the annotation tools introduced by Human Science, AnnoFab, allows customers to check progress and provide feedback on the cloud even during project execution. By not allowing work data to be saved on local machines, we also consider security.
7-4. Equipped with a security room within the company
At Human Science, we have a security room that meets the ISMS standards in our Shinjuku office. We can handle highly confidential projects on-site. We consider ensuring confidentiality to be extremely important for all projects. We continuously provide security education to our staff and pay close attention to handling information and data, even for remote projects.

 For the medical industry
For the medical industry For the automotive industry
For the automotive industry For the IT industry
For the IT industry