- Table of Contents
-
- 1. Introduction: Expectations for "AI Transforming Healthcare" and the Slow Progress
- 2. Medical AI Adoption Rates and Disparities Among Facilities Seen Through Data
- 3. The Reality of Medical AI Adoption That Does Not Progress on Ideals Alone
- 4. Efforts and Trends to Promote the Spread of Medical AI
- 5. Summary
- 6. Medical Annotation Services in Human Sciences
1. Introduction: Expectations for "AI Transforming Healthcare" and the Slow Progress
As we have mentioned several times in our company blog, "Medical × AI" is now a hot keyword frequently discussed in many media outlets. The utilization of AI in the medical field has also been repeatedly highlighted as a key strategy in government-led strategic meetings. The Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare's "Consortium for Accelerating AI Development in the Health and Medical Fields" has identified six priority areas and is focusing on accelerating AI development. These efforts are highly anticipated as a means to reduce the burden on doctors and healthcare workers and to support doctors in diagnosis and treatment. However, the reality is that the introduction of "medical AI" in actual medical settings has not progressed that much, and there remain various gaps between expectations and reality. In this blog, we would like to explain while unraveling the data.
▼Related Blogs
3 Examples of Image Diagnosis Using Medical AI
The Forefront of Medical × LLM: 6 Use Cases
2. Medical AI Adoption Rates and Disparities Among Facilities Seen Through Data
The following graph shows the status of medical AI adoption by technical field. (May 2025, Nikkei Research)
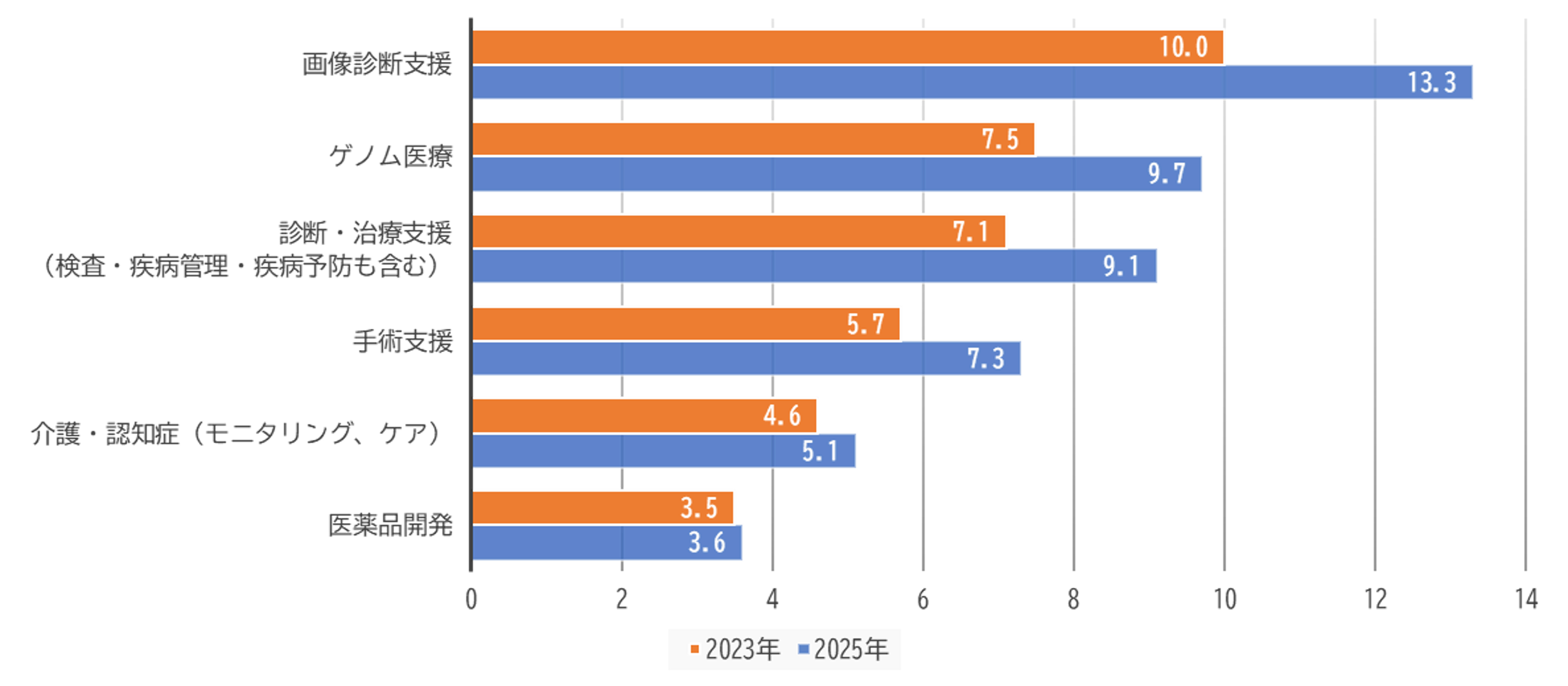
Source: Nikkei Research "Nikkei Research Medical Information System Adoption Survey <Part 1> AI steadily spreading in medical settings, but many still unsure about cost-effectiveness"
Compared to 2023, the adoption rate in 2025 shows a generally slight upward trend, with 13.3% for image diagnosis support, about 9.7% for genomic medicine, 9.1% for diagnosis and treatment support, and 7.3% for surgical support. Although the data is not shown here, the percentage of those who have "not yet introduced" is as high as 72%.
Additionally, differences in adoption rates are also noticeable depending on the size of the hospital. While image diagnosis support and genomic medicine have progressed in university hospitals and national/public hospitals, a survey conducted by Nikkei Research in July 2023 shows that 94.3% of regional clinics have not introduced these technologies.
Thus, although some advanced medical institutions have begun adopting medical AI devices, the reality is that nationwide adoption remains limited to only a portion of facilities.
▼Reference Links
Nikkei Research Medical Information System Implementation Survey <Part 1> AI steadily spreading in medical settings, but many still say "Cost-effectiveness is unclear"
Nikkei Research Medical Information System Implementation Status Survey <Part 2> Rising expectations for AI, yet 80% of medical institutions have not introduced it. The reason: "Cost-effectiveness is unclear"
3. The Reality of Medical AI Adoption That Does Not Progress on Ideals Alone
So, why is the adoption of medical AI not progressing? There are many practical challenges that cannot be resolved by ideals alone. Here again, the following shows the reasons for not introducing AI medical devices based on a survey by Nikkei Research (May 2025).
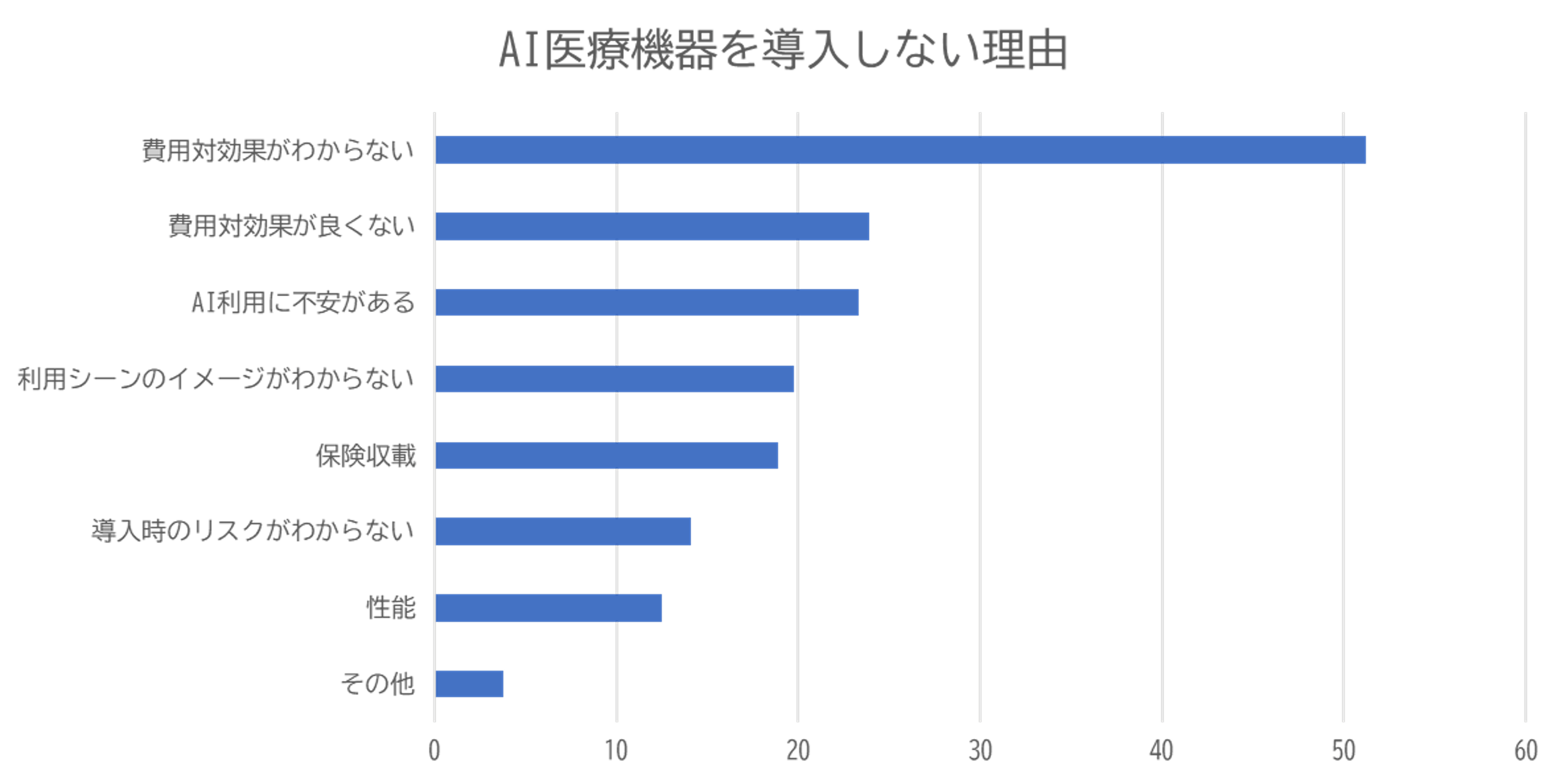
Source: Nikkei Research "Medical Information System Implementation Survey <Part 1> AI steadily spreading in medical settings, but many still say 'cost-effectiveness is unclear'"
The main reasons for "not introducing AI medical devices" are "cost-effectiveness is unclear" (51%) and "cost-effectiveness is poor" (24%), indicating that medical AI devices are expensive and face significant cost challenges. It also suggests that it is difficult to judge whether the operational improvements and diagnostic accuracy enhancements brought by medical AI justify the investment.
Next, "concerns about using AI" (23%) reflects that while there are expectations for medical AI, in reality, there is not only insufficient knowledge, information, and personnel to effectively utilize AI, but also that even if medical AI is introduced, its operation requires a certain level of knowledge acquisition and training, raising concerns about increased burdens on on-site staff.
Furthermore, about 19% responded with "insurance listing," and although there was a revision of medical fees in 2022, medical AI devices covered by insurance and listed are mainly for image diagnosis support and limited to some medical devices. This suggests that the limited availability of medical AI devices that meet the challenges and needs of medical institutions is also a barrier to the actual introduction of medical AI devices.
According to another survey*1 (a study to understand the status of medical AI adoption in clinical settings and to examine solutions to challenges for its implementation), the "reasons for not adopting medical AI products" are as follows. Although the question content differs slightly from the above, considering them comprehensively shows similar trends.
① "Currently able to operate (no problems)": 51.7% to 76.2%
② Limited to the often expensive image diagnostic medical AI devices,
"High introduction and maintenance costs": 34.3% to 38.1%
"No medical fee reimbursement": 22.6% to 23.1%
③ Risks in the use and operation of medical AI products: 0% to 4.5%
(100% safety cannot be guaranteed, no track record at other hospitals, responsibility lies with the attending physician)
④ "Cannot use the free time created by efficiency improvements for revenue-generating tasks": 0.2% to 1.5%
⑤ "AI capability is insufficient": 1.7% to 6.6%
⑥ "Labor costs are cheaper than AI": 1.5% to 4.5%
Although there is some variation among medical AI products, the relatively few negative responses regarding medical AI in points 3 to 6 above suggest that expectations and evaluations of medical AI products themselves are fairly high as tools for improving operational efficiency and supporting physicians. However, on the other hand, the large number of responses indicating "currently managing (not having problems)" implies that the chronic shortage of personnel, a common issue in the medical industry, efforts to reduce the burden on healthcare workers, and the consideration of medical AI products as a means to solve these problems have not yet been fully realized. It also suggests that there is still hesitation and a wait-and-see attitude toward the introduction of medical AI products, as it remains uncertain whether the high investment will yield commensurate benefits under the current circumstances.
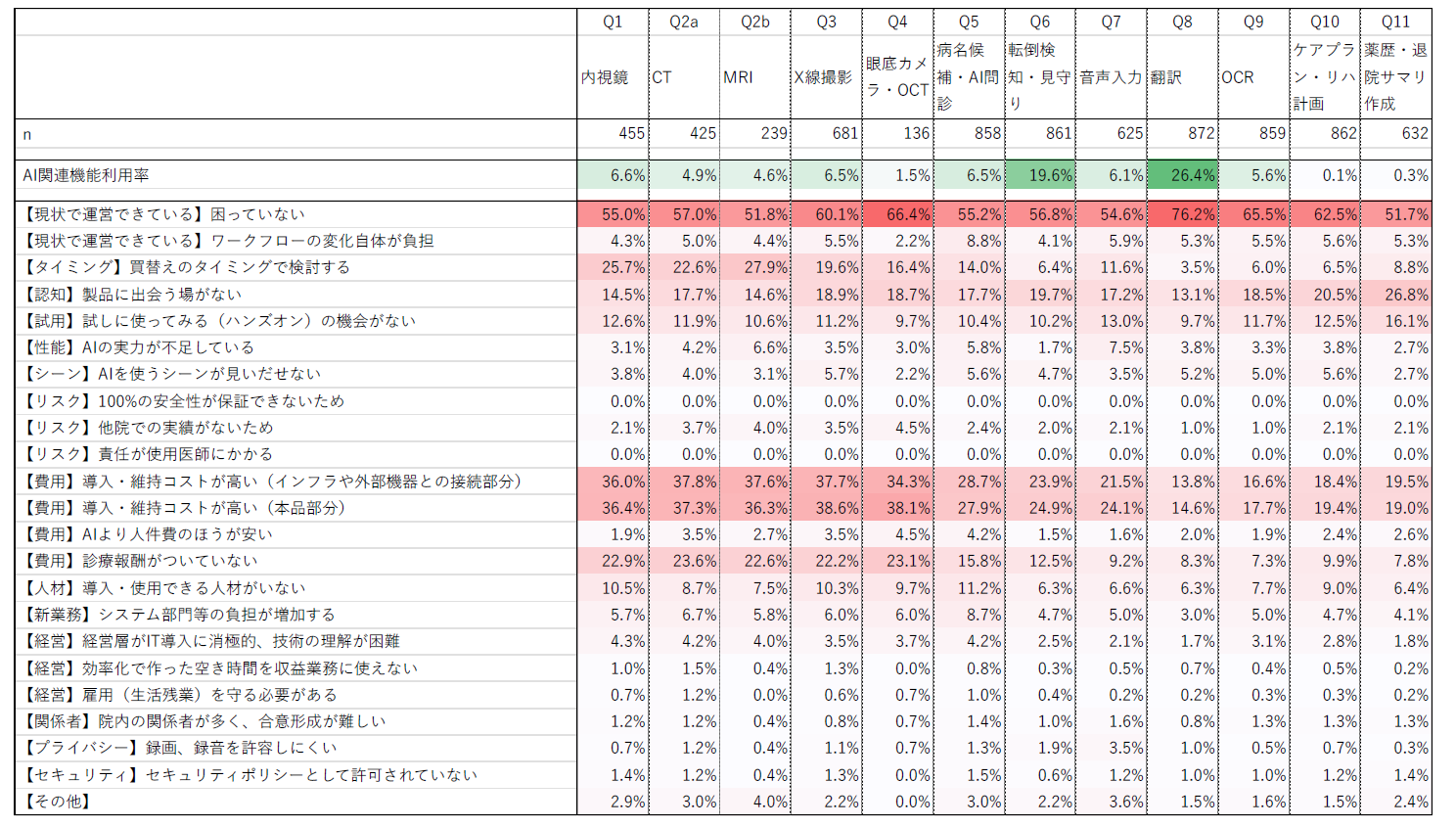
*1: Source: Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare Science Research Results Database
"Research on Understanding the Status of Medical AI Implementation in Clinical Settings and Examining Solutions to Challenges for Its Adoption"
Document Number: 202403005A (Table 7)
https://mhlw-grants.niph.go.jp/system/files/report_pdf/202403010A-sokatsu_0.pdf
▼Related Blog
Current Use of AI in Medical DX
4. Efforts and Trends to Promote the Spread of Medical AI
To address the current challenges of medical AI aimed at solving issues in the healthcare industry, various initiatives and regulatory revisions are being implemented to promote the introduction and widespread adoption of medical AI.
Medical Fee Reform:
In the 2022 medical fee revision, the revision of "Image Diagnosis Management Addition 3" increased the additional points, and a new item, "Image Artificial Intelligence Safety and Accuracy Management," was added to the facility standards eligible for medical fee additions. This indicates that the use of AI is institutionally supported and that AI is steadily transitioning from the "research and demonstration" phase to becoming a "clinical frontline asset" for medical institutions. However, since this currently applies only to some medical AI, broader application expansion is needed.
▼Reference Links
What is the Calculation of Image Diagnosis Management Addition? Secom Medical System Co., Ltd.
AI Hospital Initiative:
Led by the Cabinet Office, this project was launched with the goal of "disseminating high-quality medical AI services to many doctors and medical institutions, aiming to provide highly accurate medical services to the public and reduce the burden on healthcare workers." A "Medical AI Platform," serving as a common foundation that safely provides and utilizes big data necessary for technological development—such as linguistic data from medical institutions and medical information data from research and testing organizations—is being developed, constructed, and trial-operated jointly by private companies and the Japan Medical Association. Various efforts are underway to ensure smooth use of data and services.
▼Reference Links
What is AI Hospital?
What is AI Hospital? Introducing the Benefits and Challenges of Realizing AI Hospital / Mynavi DOCTOR
Acceleration of Approval Review and Establishment of Standards:
In Japan, the number of approvals for medical devices using AI technology (SaMD) is still low at 41 cases (as of September 2024), and reviews can take more than a year, making reform of the review system an urgent issue. The Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare's "Collaborative Plan 2024 for Optimization of Medical Device Regulation and Review" is addressing challenges aimed at optimizing reviews to provide more effective, safe, and excellent medical devices more quickly both domestically and internationally.
▼Reference Links
Collaborative Plan 2024 for Optimization of Medical Device Regulation and Review and Collaborative Plan 2024 for Optimization of In Vitro Diagnostic Drug Regulation and Review
Weak Economic Benefits, Lagging Behind Overseas... Critical Moment for the Spread of "AI Medical Devices" / News Switch
▼Related Blog
Current Status and Future Prospects of Medical AI
5. Summary
As mentioned so far, various measures are being taken to introduce, increase the adoption rate, and promote medical AI, but there are still many challenges, especially the disparity caused by the size of medical institutions, which remains a very significant issue.
As labor shortages become increasingly severe in the future, and to reduce the burden on healthcare workers and correct medical disparities, the utilization and spread of DX and medical AI are unavoidable methods. Compared to a few years ago, medical AI products have begun to penetrate, and DX has started progressing even in clinics and small to medium-sized medical institutions that make up the majority of medical facilities. However, when it comes to introducing medical AI devices for image diagnostics, which tend to be expensive even within DX, the hurdle remains high, and the current situation is that institutions inevitably have to be cautious about adoption.
6. Medical Annotation Services in Human Sciences
Extensive Experience in Medical Image Annotation
Our company has extensive experience in medical image annotation requiring skill transfer, such as surgical images and MRI images, which are highly specialized and difficult. In addition to experienced project managers for medical image annotation projects, we have many skilled workers, enabling us to deliver high-quality annotations even for projects with high difficulty and specialization that require skill transfer.
Support for Physician Supervision and Physician-led Annotation
It is understandable to have concerns about having all tasks performed solely by general workers. In such cases, we often receive requests to include physician supervision for certain checking tasks. To meet these requests, we have further strengthened our physician supervision system, enabling us to handle even more complex annotations. Additionally, if you require annotations performed by physicians rather than general workers, our project managers will provide comprehensive management services, accompanying you from resource securing to quality and progress management.
Resource management without crowdsourcing
At Human Science, we do not use crowdsourcing. Instead, projects are handled by personnel who are contracted with us directly. Based on a solid understanding of each member's practical experience and their evaluations from previous projects, we form teams that can deliver maximum performance.
Support for generative AI LLM dataset creation and structuring
In addition to creating labeled and identified training data for data organization, we also support the structuring of document data for generative AI and LLM RAG construction. Since our founding, we have been engaged in manual production as a primary business and service, leveraging our unique know-how gained from extensive knowledge of various document structures to provide optimal solutions.
Secure room available on-site
Within our Shinjuku office at Human Science, we have secure rooms that meet ISMS standards. Therefore, we can guarantee security, even for projects that include highly confidential data. We consider the preservation of confidentiality to be extremely important for all projects. When working remotely as well, our information security management system has received high praise from clients, because not only do we implement hardware measures, we continuously provide security training to our personnel.
In-house Support
We provide staffing services for annotation-experienced personnel and project managers tailored to your tasks and situation. It is also possible to organize a team stationed at your site. Additionally, we support the training of your operators and project managers, assist in selecting tools suited to your circumstances, and help build optimal processes such as automation and work methods to improve quality and productivity. We are here to support your challenges related to annotation and data labeling.

 Text Annotation
Text Annotation Audio Annotation
Audio Annotation Image & Video Annotation
Image & Video Annotation Generative AI, LLM, RAG Data Structuring
Generative AI, LLM, RAG Data Structuring
 AI Model Development
AI Model Development In-House Support
In-House Support For the medical industry
For the medical industry For the automotive industry
For the automotive industry For the IT industry
For the IT industry For the manufacturing industry
For the manufacturing industry