By thinking about what AI can do, we can see how it can be utilized in business.
In this article,
we will introduce industry-specific use cases of what AI can do for those who:
"do not know what tasks to assign to AI"
"do not know how to divide responsibilities between humans and AI"
"do not know what types of tasks are suitable for AI".
- Table of Contents
-
- 1. The Relationship between AI and Machine Learning | What is Machine Learning? Explanation of Differences from AI and the Flow of Utilization
- 1-1. The Relationship between AI, Machine Learning, Training Data, and Annotation
- 2. 12 Industry-Specific Use Cases of Machine Learning | Introduced by Image, Audio, and Natural Language Processing
- 2-1. Judging by Sight (Image Recognition)
- - Case 1: Autonomous Driving
- - Case 2: Improvement of Public Transportation Convenience
- - Case 3: Medical Support
- - Case 4: Logistics Management
- - Case 5: Inventory Management
- - Case 6: Screening for Equipment Aging
- - Case 7: Automated Document Processing
- 2-2. Listen and Decide (Speech Recognition)
- - Case 8: Music Recognition App
- - Case 9: Predictive Maintenance for Equipment Abnormalities
- 2-3. Using Words (Natural Language Processing)
- - Case 10: AI Assistant
- - Case 11: Help Desk Support
- - Case 12: Translation
- 3. Limitations and Cautions of Machine Learning | What AI Cannot Do?
- 3-1. Creative Work
- 3-2. Moral Judgment
- 3-3. Understanding Human Emotions
- 4. Current Status and Challenges of AI Implementation by Industry
- 4-1. AI Implementation Status by Industry
- 5. Reasons Why Machine Learning is Gaining Attention in Japan|Three Backgrounds Driving Its Adoption
- 5-1. Promotion of Work Style Reform
- 5-2. Realizing the Effects of Business Improvement
- 6. Concept of Machine Learning|Utilization Beyond Case Studies
- 7. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)|Common Questions About Machine Learning
- 8. Human Science Teacher Data Creation, LLM RAG Data Structuring Outsourcing Service
1. The Relationship between AI and Machine Learning | What is Machine Learning? Explanation of Differences from AI and the Flow of Utilization
1-1. The Relationship between AI, Machine Learning, Training Data, and Annotation
To understand what AI can do, let's first organize how AI works. To operate AI, it is necessary for humans to provide data for it to learn. By repeatedly supplying data that includes information about problems and answers, AI develops the ability to discern patterns and characteristics from that data. This training is called machine learning. Below, we will organize commonly used terms.
AI: Refers to artificial intelligence itself.
Machine Learning: Training for AI to operate.
Training Data: Data used for machine learning.
Annotation: The task of creating training data.
The process of AI development is illustrated in this way.

For more about annotation
>> What is annotation? Explanation from its meaning to its relationship with AI and machine learning.
For more about training data
>> What is training data? Explanation from its relationship with AI, machine learning, and annotation to how to create it.
Examples of Business Efficiency Improvement Using AI
>> Improving Business Efficiency with AI Utilization. Four Case Studies of Machine Learning Projects Where 80% Experienced Benefits.
2. 12 Industry-Specific Use Cases of Machine Learning | Introduced by Image, Audio, and Natural Language Processing
As AI continues to learn and develop judgment capabilities, it becomes possible to delegate various tasks. From here, we will introduce examples of utilization by industry based on what AI can do.
2-1. Judging by Sight (Image Recognition)
You can view images and videos to identify where things are located. It is also possible to track the movement of the subject.
Case 1: Autonomous Driving
In autonomous driving and driver assistance, AI identifies oncoming vehicles, pedestrians, traffic signs, and more from in-vehicle camera footage. In addition to the 2D method using regular video, the use of 3D data obtained by LiDAR (Light Detection And Ranging) is also progressing.
Case 2: Improving Convenience of Public Transportation
By having AI grasp the usage status of public transportation, the safety and convenience for passengers are enhanced. Recently, there have also been attempts to avoid crowding by simulating human flow and travel time.
>> Hitachi Launches Service to Avoid Crowding Using AI and Simulation Technology
Case 3: Medical Support
AI is being utilized to improve the efficiency of diagnostic tasks. AI extracts areas suspected to be lesions or tumors from X-ray, ultrasound, and MRI images. Google's medical image recognition AI recognizes lesions from skin images taken with a smartphone and performs diagnoses.
>> Challenges to the practical application of Google's "medical" image recognition AI
Case 4: Logistics Management
It is utilized in warehouse management tasks such as inspection and sorting. AI recognizes the quantity of cardboard boxes and the labels on them to automatically sort items. It also recognizes the movements of on-site workers, helping to improve workflow paths.
Case 5: Inventory Management
Utilized in the retail industry for managing in-store inventory. Automatically grasps the status of stock and shortages from images of product shelves.
Case 6: Screening for Equipment Aging
Extracts features such as paint peeling and cracks from images of buildings and equipment to identify signs of aging.
>> Inspection of steel towers using drones and AI – Deputy Minister Fumiaki Kobayashi of the Digital Agency inspects ahead of regulatory reforms
Case 7: Automatic Document Processing
Contracts and invoices are converted to text using AI OCR, automating record-keeping and calculations. It also supports handwritten characters.
2-2. Listen and Decide (Speech Recognition)
It listens to audio and performs identification.
Case 8: Music Recognition App
It recognizes songs playing around and displays the title and artist name (e.g., Shazam).
Case 9: Predictive Maintenance for Equipment Abnormalities
Learns the normal sounds of equipment and detects anomalous noises as outliers to identify abnormalities early.
2-3. Using Words (Natural Language Processing)
It understands the meaning of words used by humans and can also compose text and speak.
Case 10: AI Assistant
It interprets intentions through speech recognition × natural language processing and responds to requests.
Case 11: Help Desk Support
The chatbot understands inquiry texts and responds appropriately.
>> AI listens to the purpose of calls to the call center, and TMJ provides an automated voice response service
Case 12: Translation
Recognizes text in text or images and translates it (e.g., sequential translation with a camera).
3. Limitations and Cautions of Machine Learning | What AI Cannot Do?
So far, we have looked at examples of AI applications, but there are also areas where it is difficult for AI to achieve results.
3-1. Creative Work
The output of generative AI is generated based on past data and differs from human creativity based on intuition and unique experiences. It is used as a complementary tool for creativity.
3-2. Moral Judgment
Ethical judgment is not inherent in AI, so humans are responsible for checking and improving biases in the training data.
3-3. Understanding Human Emotions
AI does not possess emotions or consciousness, so it cannot understand emotions or empathize.
4. Current Status and Challenges of AI Implementation by Industry

4-1. AI Implementation Status by Industry
This is data that surveys the status of AI implementation by industry.
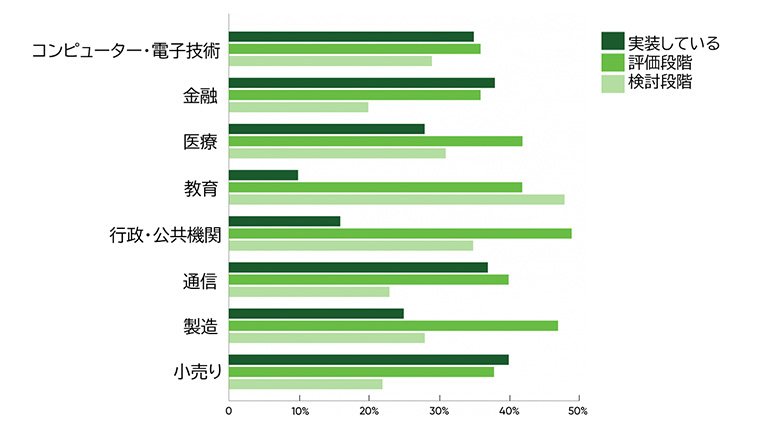
Source: Created by the author from O'Reilly AI Adoption in the Enterprise 2021
While implementation is progressing in computers, finance, and retail, education and administration have low implementation rates, and ethical issues such as personal information, social roles, and environmental considerations tend to be challenging.
5. Reasons Why Machine Learning is Gaining Attention in Japan|Three Backgrounds Driving Its Adoption

The main reasons why AI adoption is attracting attention in Japan are as follows.
5-1. Promotion of Work Style Reform
By delegating simple tasks to AI, humans can spend more time on planning and learning.
5-2. Realizing the Effects of Business Improvement
A survey of companies that have introduced AI shows that more than 80% have experienced its effectiveness.
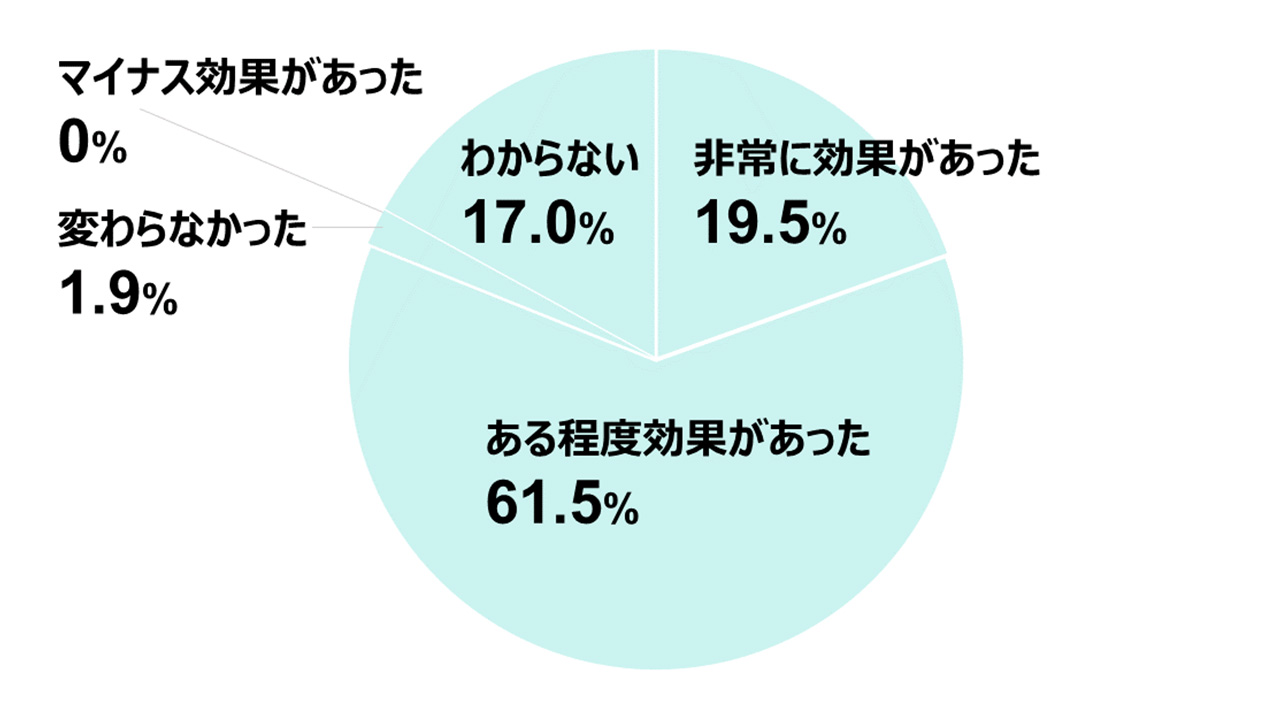
Source: Created by the author based on the 2021 White Paper on Information and Communications by the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications
6. Concept of Machine Learning|Utilization Beyond Case Studies
When considering AI implementation, many companies probably refer to "existing case studies." However, case studies are merely examples of past successes and may not be directly applicable to your own company. What is more important is the perspective of identifying "where the unique opportunities for utilization within your own company lie" while referencing these case studies.
For example,
・If this process were entrusted to AI, how much would productivity improve?
・If this task could be automated, to which new areas could personnel be redirected?
・To what extent can AI expand new approaches to improve customer experience?
Asking such questions becomes the first step in implementation.
By combining multiple technologies such as image recognition, speech recognition, and natural language processing, AI enables applications beyond existing case examples. In other words, clearly defining "what problems you want to solve" and designing AI's role by working backward from there leads to differentiation and competitive advantage.
Rather than simply following existing examples, use them as a starting point to develop your company's unique ideas. This can be said to be the key to successfully implementing AI.
7. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)|Common Questions About Machine Learning
Q1. How much does machine learning cost?
A. The cost varies greatly depending on the scale and purpose of the project, so it cannot be generalized. If internal resources are allocated to organizing your own data and annotation, these tasks must be performed in addition to regular duties, which incurs additional costs. Even in such cases, outsourcing to external vendors can sometimes allow for more efficient progress. Also, starting with a small-scale PoC can help verify effectiveness while minimizing risk.
Q2. Is it possible to implement AI even if our company does not have experts in AI or data science?
A. Implementation may be possible even without specialized knowledge. Recently, the number of AI tools available with no-code or low-code options has increased, significantly lowering the barriers for non-engineers to train AI models and develop applications. Additionally, many companies outsource tasks such as creating training data and model development to external partners even if they lack in-house experts.
Q3. What is the first step to take when starting with machine learning?
A. It is important to first clearly define "which business problem you want to solve." After that, conducting a PoC using a small dataset to verify its effectiveness before moving on to full-scale implementation is a flow that reduces the risk of failure. Rather than aiming for large-scale implementation right away, it is better to proceed step by step.
Q4. How can data security and confidentiality be ensured?
A. When outsourcing data externally, it is important to choose vendors that have systems in place such as ISMS certification and dedicated security rooms. By requesting companies that manage contracted workers rather than using crowdsourcing, you can significantly reduce risks. It is also crucial to confirm whether access control, management, and security training for workers are thoroughly implemented, even in remote environments.
8. Human Science Teacher Data Creation, LLM RAG Data Structuring Outsourcing Service
Over 48 million pieces of training data created
At Human Science, we are involved in AI model development projects across various industries, starting with natural language processing, including medical support, automotive, IT, manufacturing, and construction. Through direct transactions with many companies, including GAFAM, we have provided over 48 million high-quality training data. We handle a wide range of training data creation, data labeling, and data structuring, from small-scale projects to long-term large projects with a team of 150 annotators, regardless of the industry.
Resource management without crowdsourcing
At Human Science, we do not use crowdsourcing. Instead, projects are handled by personnel who are contracted with us directly. Based on a solid understanding of each member's practical experience and their evaluations from previous projects, we form teams that can deliver maximum performance.
Generative AI LLM Dataset Creation and Structuring, Also Supporting "Manual Creation and Maintenance Optimized for AI"
In addition to labeling for data organization and creating training data for identification-based AI, we also support structuring document data for generative AI and LLM RAG construction. Since our founding, manual production has been our main business and service, and we now also assist with organizing business knowledge and manual creation aimed at future generative AI and RAG implementation and utilization. We provide optimal solutions leveraging our unique expertise in the structure of various documents.
Secure room available on-site
Within our Shinjuku office at Human Science, we have secure rooms that meet ISMS standards. Therefore, we can guarantee security, even for projects that include highly confidential data. We consider the preservation of confidentiality to be extremely important for all projects. When working remotely as well, our information security management system has received high praise from clients, because not only do we implement hardware measures, we continuously provide security training to our personnel.
In-house Support
We provide staffing services for annotation-experienced personnel and project managers tailored to your tasks and situation. It is also possible to organize a team stationed at your site. Additionally, we support the training of your operators and project managers, assist in selecting tools suited to your circumstances, and help build optimal processes such as automation and work methods to improve quality and productivity. We are here to support your challenges related to annotation and data labeling.

 Text Annotation
Text Annotation Audio Annotation
Audio Annotation Image & Video Annotation
Image & Video Annotation Generative AI, LLM, RAG Data Structuring
Generative AI, LLM, RAG Data Structuring
 AI Model Development
AI Model Development In-House Support
In-House Support For the medical industry
For the medical industry For the automotive industry
For the automotive industry For the IT industry
For the IT industry For the manufacturing industry
For the manufacturing industry