In December 2015, a report was published through joint research between the Nomura Research Institute and the University of Oxford stating that 49% of jobs in Japan would disappear within 10 to 20 years due to the introduction of AI. Now, seven years later, are human jobs really being stolen by AI? If the introduction of AI accelerates from here, what skills will be required of the remaining human workforce? This article will examine the current situation as it compares to the implications of that report and consider what skills will be needed for future workers and the new jobs created by AI.
- Table of Contents
-
- 1. Current State of AI Implementation
- 1-1. The rate of AI implementation by Japanese companies is still low.
- 1-2. Human workers are necessary to develop AI.
- 2. Why AI Takes Jobs
- 2-1. Strengths of an AI workforce
- 2-2. The evolution of AI beyond mere automation
- 3. What Jobs Will AI Erase and What Jobs Will Remain
- 3-1. Jobs replaced by AI
- 3-2. Jobs that require human work
- 3-3. Consider what things only humans can do
- 4. New Jobs Created by AI
- 4-1. Data scientist
- 4-2. AI engineer
- 4-3. Annotator
- 5. AI Consultations with Human Science
- 5-1. 48 million items of training data created
- 5-2. Resource management without crowdsourcing
- 5-3. The latest data annotation tools
- 5-4. Secure room in office
1. Current State of AI Implementation

Seven years have passed since experts made a startling prediction about Japanese employment, but are human jobs actually being stolen by AI?
1-1. The rate of AI implementation by Japanese companies is still low.
From left to right, the following chart shows the percentage of companies in Japan, Germany, and the United States that answered yes to a survey asking whether they are utilizing AI technology in their operations.
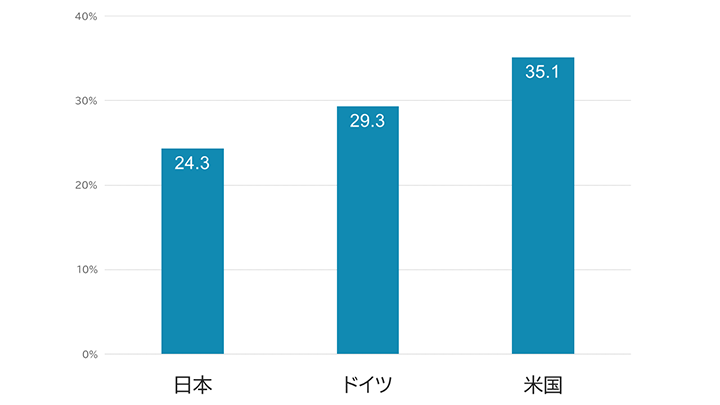
Source: Image created by the author, based on a 2021 research study by the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications on the economic impact of digital transformation.
While this data is from 2021, the AI utilization rate among Japanese companies is still surprisingly low at 24.3%. It shows that the actual use of AI is not progressing as much as expected. The predicted figure of 49% may be considered alarmist in this context, but it is true that the adoption of AI is advancing year by year. Therefore, our takeaway from those early predictions should be that certain trends will impact the jobs that are at high risk of being taken over by AI, as opposed to those that will still require human work. We must consider measures that take this split into account and think about the skills that humans should acquire moving forward.
1-2. Human workers are necessary to develop AI.
Human labor is essential to the task of developing AI that can be implemented at the business level. There is a lot of manual work involved in effective machine learning and the preliminary process known as annotation. The reason why the implementation of AI has been slower than predicted in 2015 may also lie in such factors.
2. Why AI Takes Jobs

2-1. Strengths of an AI workforce
The appeal of using AI as a workforce is its accuracy and speed. Just like when implementing manufacturing machines, once AI learns how to perform a task, it can continue that task indefinitely. Unlike with human labor, the accuracy does not decline due to fatigue, and working hours are unregulated. The introduction of AI is expected to significantly improve productivity and operational efficiency.
2-2. The evolution of AI beyond mere automation
Furthermore, AI has unique strengths. Unlike robotic process automation (RPA) and similar technologies, AI can flexibly respond not only to fixed tasks but also to variation in the content of the work. AI can also manipulate language. AI that automatically generates advertising copy can instantly create a large volume of copy by analyzing product information, past copy, news, and online reviews. AI can suggest ideas based on the materials provided and execute freeform tasks. You could say that the strengths of AI, unlike traditional mechanization and simple automation, lie in this flexibility.
For more information on the differences between AI and RPA, check out the link below.
>> The Basics of RPA. How Does It Differ from AI? Introducing How to Use RPA and AI in Tandem.
3. What Jobs Will AI Erase and What Jobs Will Remain
Let's take a look at the specific professions mentioned in the report from 2015.
3-1. Jobs replaced by AI
Jobs that involve a lot of formulaic processes are at high risk of being taken over by AI. From the perspective of operational efficiency, theorists predict that humans will have a harder time holding on to these jobs in the future.
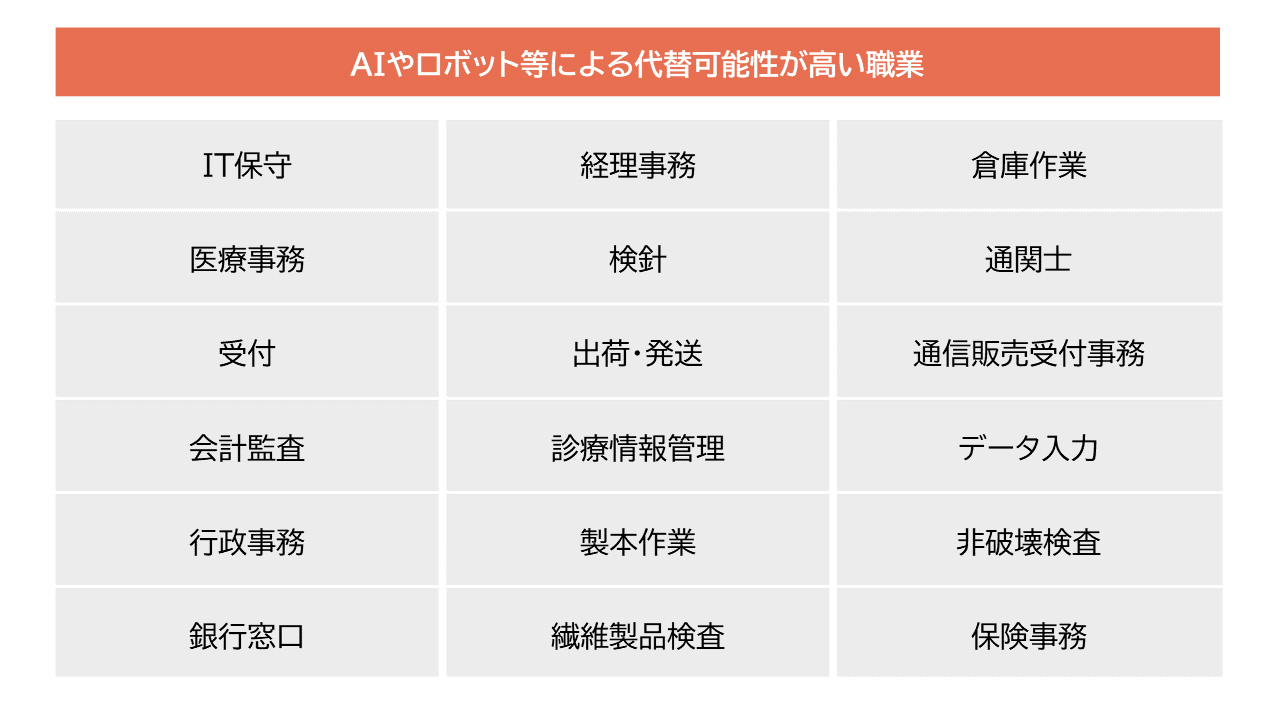
Source: Image created by author based on "49% of Japan's Labor Force Could Be Replaced by Artificial Intelligence and Robots" by the Nomura Research Institute (NRI) in 2015
3-2. Jobs that require human work
Jobs related to the human body and mind, as well as those requiring creativity, are said to be less vulnerable to being taken over by AI.
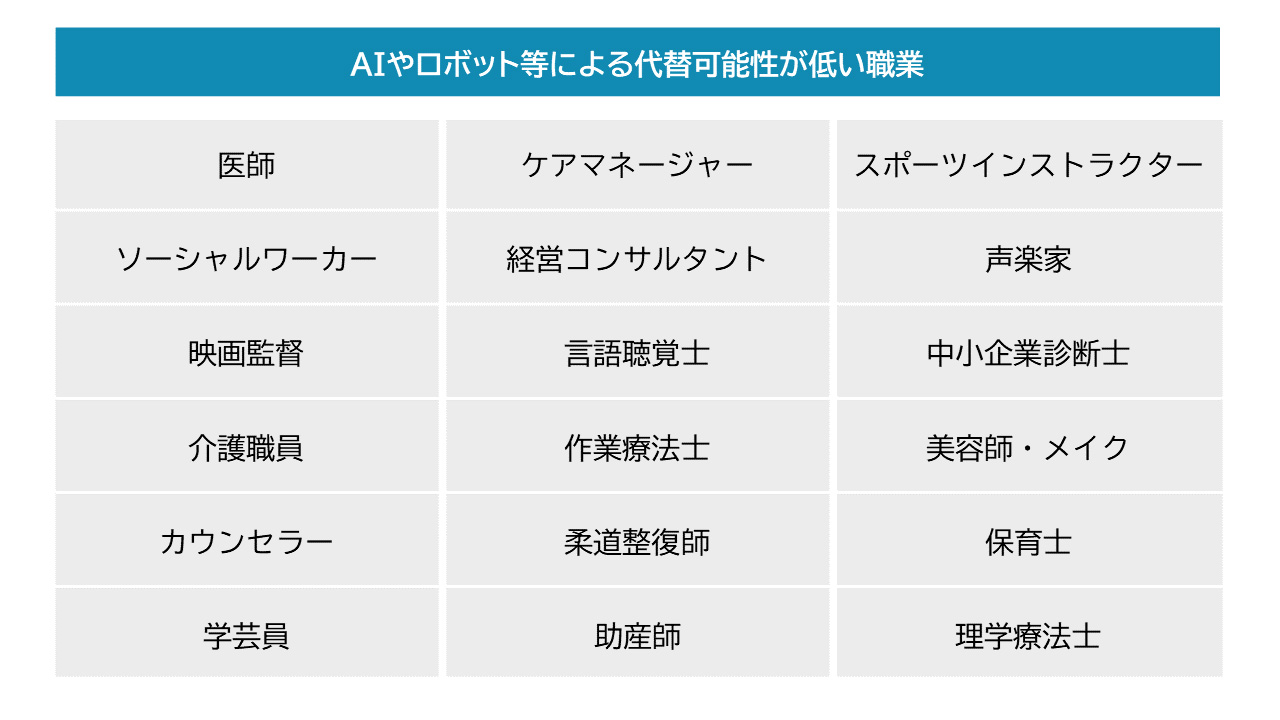
Source: Image created by author based on "49% of Japan's Labor Force Could Be Replaced by Artificial Intelligence and Robots" by the Nomura Research Institute (NRI) in 2015
3-3. Consider what things only humans can do
Current AI has evolved beyond mere automation and reached a level where it can analyze big data and suggest responses tailored to the situation. However, it cannot create things from scratch. Skills such as planning and creativity will continue to require human effort. Adaptability, critical thinking, and leadership, which are related to communication and relationship building, are still areas where humans excel. By reconsidering what things only humans can do, we may gain insight into future work methods.
4. New Jobs Created by AI

Although some jobs may disappear due to the spread of AI, new jobs are also being created, and the demand for certain roles is increasing. When considering how people will find work in the age of AI, let's also pay attention to these positive aspects.
4-1. Data scientist
A data scientist is a person who analyzes data based on statistics and algorithms to create value and solve problems. One major challenge in AI development is to perform proper analysis and classification on vast amounts of data and to identify what role this data plays in improving the accuracy of AI.
4-2. AI engineer
These workers are also called ML (Machine Learning) engineers. They play a crucial role in the development of AI by actually training the machines and building the systems that enable AI to function.
4-3. Annotator
The development of AI relies on a process called machine learning. Annotators are responsible for the practical work of creating the training data used in this process. They manually tag and label large amounts of data based on accurate knowledge and evaluation standards. This role has a significant impact on the quality of AI.
For more on annotation
>>What Is Annotation and Its Relationship to AI and Machine Learning?
For more on training data
>>What Is Training Data? Everything from Its Relationship with AI, Machine Learning, and Annotation to How to Create It.
5. AI Consultations with Human Science
5-1. 48 million items of training data created
"I want to implement AI, but I don’t know where to start."
"I don’t know what to request, even if I outsource."
If your company is struggling with either of these issues, please feel free to contact Human Science. Our company has been involved in AI model development projects across various industries, starting with natural language processing and extending to medical support, automobiles, IT, manufacturing, and construction, just to name a few. Through direct business with many companies, including GAFAM, we have provided over 48 million pieces of high-quality training data. No matter the industry, our team is prepared to handle anything from small-scale annotation projects to long-term ventures with 150 annotators.
>> Human Science’s Annotation Services
5-2. Resource management without crowdsourcing
At Human Science, we do not use crowdsourcing. Instead, projects are handled by personnel who are contracted with us directly. Based on a solid understanding of each member's practical experience and their evaluations from previous projects, we form teams that can deliver maximum performance.
5-3. The latest data annotation tools
One of the annotation tools introduced by Human Science is AnnoFab, which lets you receive progress checks and customer feedback on the cloud, even while the project is ongoing. By ensuring that work data cannot be saved on local machines, we demonstrate appropriate security measures.
5-4. Secure room in office
Human Science has a secure room that meets ISMS standards within our Shinjuku office, so we can handle even highly confidential projects on-site. The promise of of confidentiality is extremely important to us for any of our projects. We provide continuous security training to our staff, and we handle all information and data with the utmost care, even on remote projects.

 Text Annotation
Text Annotation Audio Annotation
Audio Annotation Image & Video Annotation
Image & Video Annotation Generative AI, LLM, RAG Data Structuring
Generative AI, LLM, RAG Data Structuring
 AI Model Development
AI Model Development In-House Support
In-House Support For the medical industry
For the medical industry For the automotive industry
For the automotive industry For the IT industry
For the IT industry For the manufacturing industry
For the manufacturing industry