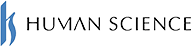Quality Control for Japanese Translation and Localization
At Human Science, we achieve high-quality translations through a multi-layered quality management system that complements each other in three stages: (1) recruitment and management of translators, (2) development of glossaries and style guides, and (3) reviews by dedicated reviewers.
▼ Thorough Management System for Translators
▼ Glossaries and Style Guides to Achieve High Quality
▼ Full Reviews by Dedicated Reviewers and Utilization of Check Tools
Thorough Management System for Translators
Human science translators are experts in their respective fields who have passed a unique translation trial (test). The pass rate for trials in Japanese translation and localization is a narrow gate at approximately 8 percent.
Additionally, when assigning translators to a project, we carefully listen to the client's work and quality requirements in advance, and based on our extensive data and know-how accumulated over the years, we meticulously select the most suitable translator.
Even if it is a similar field,
- Whether the translation target is a "manual", a "catalog", or a "technical document"
- Whether the target audience is "general users" or "technicians"
- What our customers seek is either a 'natural translation' or a 'literal translation'.
This is because the translators to be selected vary depending on factors such as.
- Translator Recruitment and Management
Process -
At Human Science, we implement a consistent process for the recruitment of translators and their management within projects.
- Trial Procedure
-
- 1. The trial will be conducted using original problem statements from Human Science. Although it is a small translation test consisting of a few hundred words, we take the time to carefully craft the questions in order to assess the translator's abilities. Additionally, to ensure that the translator's knowledge is up-to-date, we regularly change the problem statements.
Trial Categories: "IT", "Marketing", "Business Documents", "Contract Documents", "Video" - 2. Our in-house team of technical reviewers and linguistic reviewers conduct checks using the same criteria and perspectives as in regular translation projects, and the review team deliberates to determine pass or fail (pass rate: 8%).
>>Quality Control 3 (Full review by dedicated reviewers and utilization of checking tools) - 3. We have compiled the trial scores, trends, and areas of expertise of registered translators into a database.
- 1. The trial will be conducted using original problem statements from Human Science. Although it is a small translation test consisting of a few hundred words, we take the time to carefully craft the questions in order to assess the translator's abilities. Additionally, to ensure that the translator's knowledge is up-to-date, we regularly change the problem statements.
- Evaluation Criteria During Trial
5 Trial Evaluation Items
①Translation Quality - ・Check for any mistranslations
- ・Are there any unnatural expressions used?
- - Are appropriate styles and terms being used?
②Notation - ・Check for spelling mistakes and translation omissions
- ・Check for the absence of double-byte characters and double spaces
- ・Is the value correct?
- - Whether the specified terms are used
- ・Are the correct symbols (quotation marks, parentheses, etc.) used?
- ・Check for spelling mistakes and translation omissions
③Specialized Knowledge Do you have background knowledge in the trial target field?
④ Responsiveness - ・Is communication via email and other means appropriate?
- ・Check for any missing delivery data or submitted materials
- ・Is there any communication regarding unclear points or areas where exception handling was performed?
⑤Project Achievements Do you have sufficient translation experience?
- Project Start
-
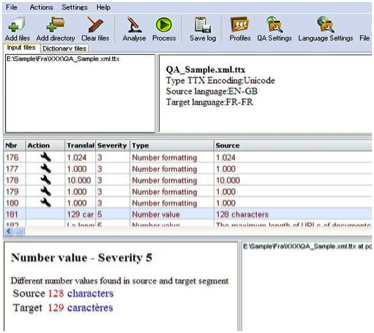
- ① Confirm work requirements and quality requirements with the client
- ②Select translators that match the following elements from the database
Area of expertise
Work experience - ③ Assign projects to translators with high past evaluations
※ Based on past performance, translators are managed using a four-tier evaluation system: "Rank AA", "A", "B", and "No Evaluation".
- Project Completion
-
- ① Summarize error detection status and customer requests, and provide feedback to the translator
- ②Register the error detection status in the online translator database and accumulate it as shared information
- Information Management
-
Regarding the management of confidential information (ISMS, training, access control, security room), please see here
Glossary and Style Guide for Achieving High Quality
A major factor that influences the quality of translation is the consistency of terminology and style. No matter how beautifully the translation is rendered, if the terminology and style are inconsistent, the intent of the text may not be conveyed correctly, leading to misunderstandings and various issues.
Especially when translating large volumes of documents, it is common to divide the work among multiple translators, so it is important to maintain consistency in terminology and style throughout the entire project.
At Human Science, we review the source documents before translation as needed, thoroughly identifying the terms and styles that should be standardized, and create a glossary and style guide.
- What is a glossary?
-
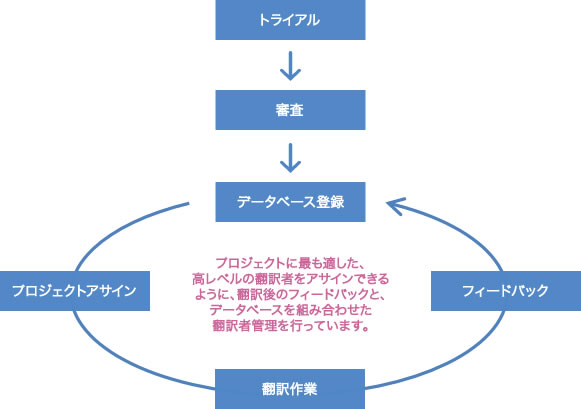
This is a list of terms used for translation. By creating a glossary that defines consistent translations for product names and technical terms before translation, you can ensure that consistent terminology is used throughout the document.
(For example) Without a glossary, the translations will be inconsistent, leading to confusion.
In particular, when translating a substantial amount of text with multiple translators, without a glossary, the terms used may differ among translators, leading to inconsistencies in terminology.
At Human Science, we identify the terms that need to be standardized before translation and create a glossary to prevent inconsistencies and errors in the translated terms.
If you have specific terms you would like us to use, please provide them before translation, and we will include those terms in the glossary for the translation.
- Examples of items to include in the glossary
-
- ●Provided Glossary (terms with specified translations such as parts, company names, product names, function names, etc.)
- ●Terms not included in the provided glossary
・Terms related to newly implemented features and technologies
・Text that does not require translation (such as file extensions and program code) - ●Verb
- ●Unit Symbol
- ●Other Frequently Used Terms
- etc.
- What is a Style Guide?
-
This is a list of rules regarding the style (expressions, notation, grammar, etc.) to be used in translation.
Similar to a glossary, establishing rules for style before translation allows for consistency throughout the document, thereby improving translation quality.
(For example) Without a style guide, the notation and expressions will become inconsistent.
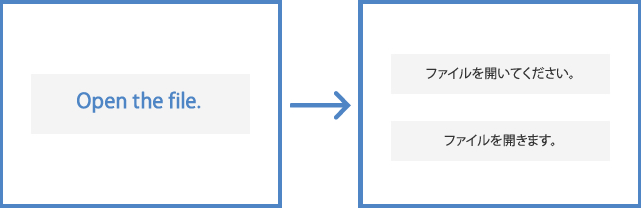
At Human Science, we create style guides for each client and project before translation, providing our customers with consistent, high-quality translations throughout the document. Since the representation of symbols and numbers varies by language, we create style guides according to the rules of each language.
- Content to Include in the Style Guide (Example)
-
- ●Customer-Specified Rules
-
- Use of uppercase and lowercase letters
・Number format (thousands separator, decimal point)
- Notation of symbols and signs (quotations, apostrophes, parentheses, etc.)
- Writing Style
- Style of warning and caution statements
Reference Document Style
●Rules for Each Language
-
Full review by dedicated reviewers and utilization of check tools
In translations of manuals and brochures, errors in numbers, unit symbols, and standard phrases can lead to serious problems and undermine user trust.
At Human Science, we have a dual system of checks by both humans and tools to prevent errors.
By having a system that maintains quality across the entire team, rather than relying solely on the quality control of individual translators, we continue to provide stable quality even for large-scale projects.
- Full review by a dedicated reviewer
-
Dedicated technical reviewers and linguistic reviewers will conduct a full review by comparing the original text with the translated text.
An example of review items
・Mistranslation
・Omission
・Formatting errors
・Careless mistakes
・Client specifications
・Reuse processing
・Pending processing
・Japanese expressions
A skilled team of reviewers, including those with extensive experience as SEs, reviewers with programming experience, and veteran reviewers who have been reading Japanese in the IT industry for 16 years, will handle various projects.
If you have a short deadline and need to assign multiple translators, want to create technically accurate documents, or wish to make the text more natural in Japanese, please feel free to consult us with any requests.
- Quality Management Using Tools
-
At Human Science, we conduct translation checks for notation and terminology using Trados and our proprietary original tools. We also reliably prevent errors like those listed below, which may not be caught by human eyes.
- Are there any spelling mistakes?
- Do the numbers in the original text match the numbers in the translated text?
- Are the terms specified by the customer being used appropriately?
After delivery, we will not impose the burden of formal checks on values and unit symbols on your side.
In particular, when a large volume of translation is divided among multiple translators in a short period of time, tools are effective in checking for consistency in notation and terminology among the translators.
Comparison of Human Checks and Tool Checks
Checklist (Example) Human
Check
(Visual Inspection & Search
etc.)Check by tools Notation
・Double Byte・Double Space
・Missing period at the end of the sentence
Duplicate Symbols
- Full-width symbols
△ ○ Terminology and Standard Phrases △ ○ Check for translation omissions, multiple translations, multiple source texts, and numerical representations
・Brackets
Tab
・Consistency of capital letters at the beginning of sentences
- Spaces before and after unit symbols
Language Rules
Spaces before and after symbols
- Number Format
・Quotation marks
△ ○ Spelling Mistake △ △ ○… Checkable
△… Partially checkable (There is a possibility of missing checks in case of manual checks)
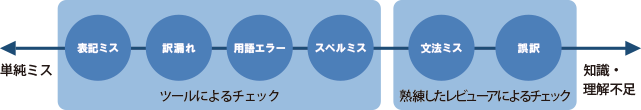
Differences in the scope of checks by humans and checks by tools
- Check tools to use (e.g.)
-
We use multiple tools such as Trados QA Checker, QA Distiller, Xbench, and our proprietary tool UI Checker to detect errors according to the purpose.
The specific checklist items will be customized by the localization engineer for each project according to the style guide and translation content. If there are items that require focused checking, please let us know in advance.
For those who want to know more about Translation and Localization into Japanese
- Reception hours: 9:30 AM to 5:00 PM JST
Tokyo: +81-3-5321-3111 Nagoya: +81-52-269-8016